Abstract
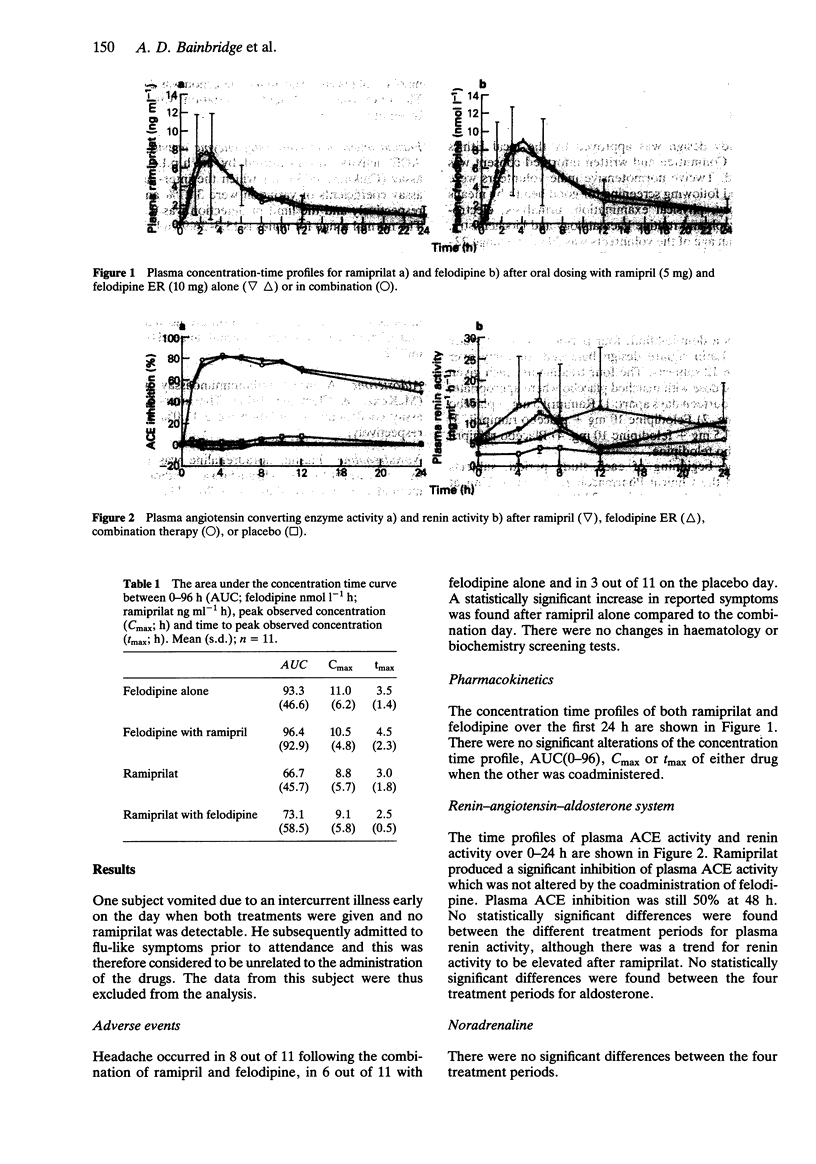
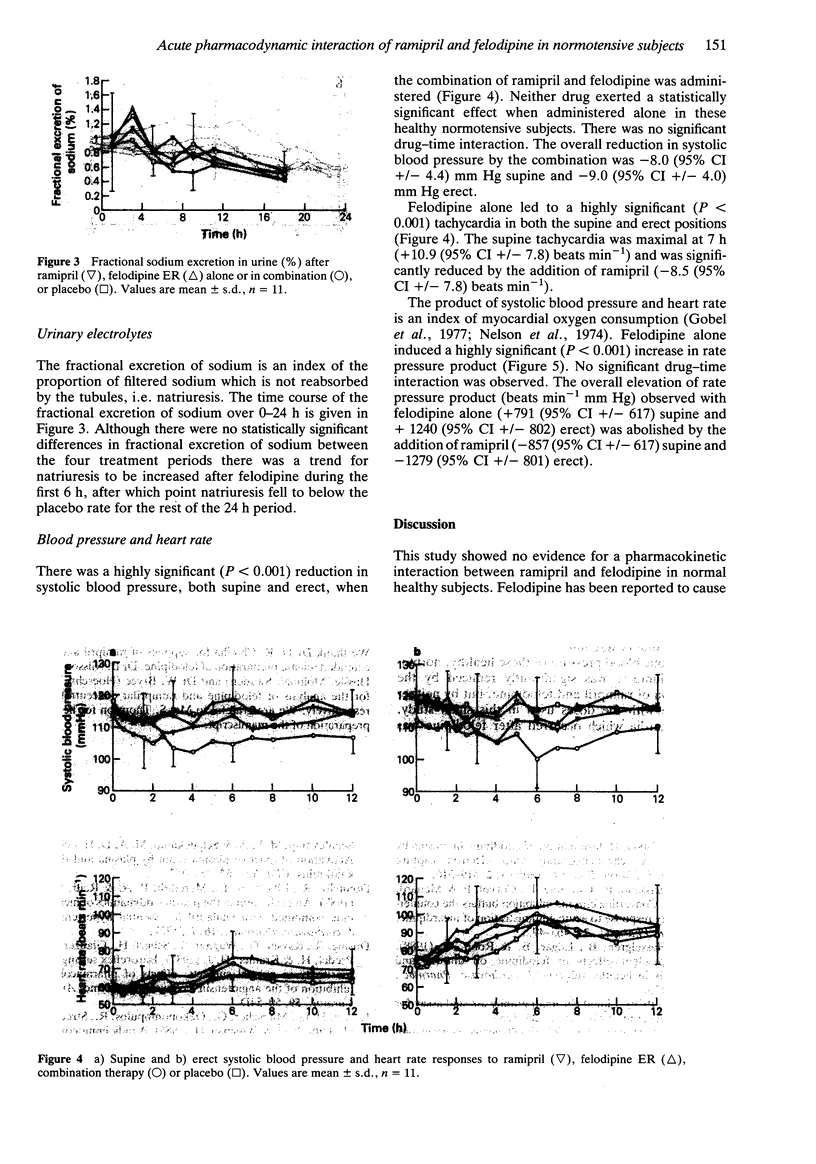
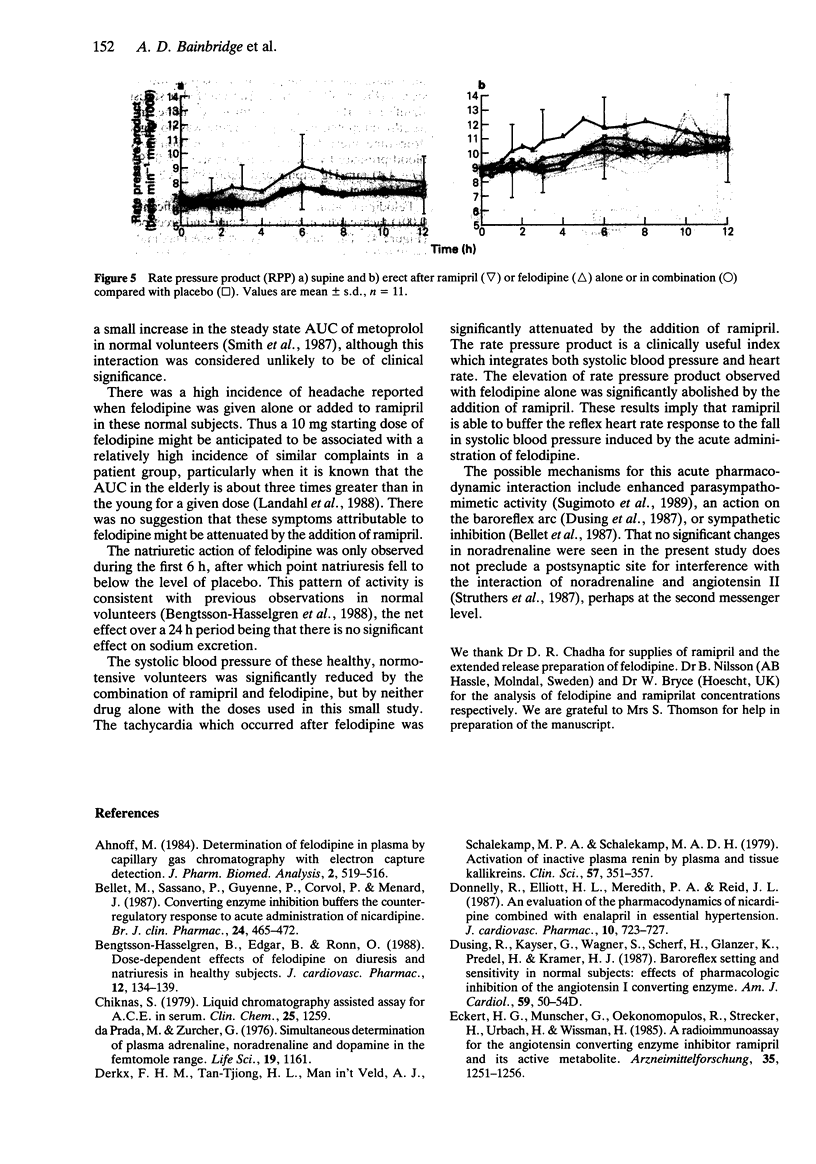
1. The possibility of an acute pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interaction between the ACE inhibitor ramipril and the calcium antagonist felodipine was examined in 12 normotensive male volunteers. 2. Ramipril (5 mg) and felodipine ER (10 mg) were administered orally in a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, Latin square design to fasting subjects. 3. There was no evidence of a pharmacokinetic interaction between agents. The concentration-time profiles remained unaltered by coadministration of both agents. 4. Plasma ACE inhibition by ramiprilat was unaffected by concurrent felodipine. The trend towards increased fractional sodium excretion after felodipine was not influenced by ramipril. Plasma renin activity, aldosterone and catecholamines remained unaltered. 5. Combination therapy produced a statistically significant fall in blood pressure supine and erect which was not evident with monotherapy. The reflex tachycardia associated with felodipine monotherapy was significantly attenuated by the coadministration of ramipril. 6. This study presents further evidence for the effective combination of ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists to lower blood pressure. The reflex tachycardia associated with calcium antagonist therapy can be significantly reduced by coadministration with sustained antihypertensive effect.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnoff M. Determination of felodipine in plasma by capillary gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1984;2(3-4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0731-7085(84)80055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellet M., Sassano P., Guyenne T., Corvol P., Menard J. Converting-enzyme inhibition buffers the counter-regulatory response to acute administration of nicardipine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;24(4):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson-Hasselgren B., Edgar B., Rönn O. Dose-dependent effects of felodipine on diuresis and natriuresis in healthy subjects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;12(2):134–139. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198808000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiknas S. G. A liquid chromatography-assisted assay for angiotensin-converting enzyme (peptidyl dipeptidase) in serum. Clin Chem. 1979 Jul;25(7):1259–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Zürcher Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkx F. H., Tan-Tjiong H. L., Man in 't Veld A. J., Schalekamp M. P., Schalekamp M. A. Activation of inactive plasma renin by plasma and tissue kallikreins. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Oct;57(4):351–357. doi: 10.1042/cs0570351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly R., Elliott H. L., Meredith P. A., Reid J. L. An evaluation of the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of nicardipine combined with enalapril in essential hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;10(6):723–727. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198712000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert H. G., Münscher G., Oekonomopulos R., Strecker H., Urbach H., Wissmann H. A radioimmunoassay for the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor ramipril and its active metabolite. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(8):1251–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B., Regårdh C. G., Lundborg P., Romare S., Nyberg G., Rönn O. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of felodipine in healthy subjects after various single, oral and intravenous doses. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1987 May-Jun;8(3):235–248. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2510080305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobel F. L., Norstrom L. A., Nelson R. R., Jorgensen C. R., Wang Y. The rate-pressure product as an index of myocardial oxygen consumption during exercise in patients with angina pectoris. Circulation. 1978 Mar;57(3):549–556. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.57.3.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guazzi M. D., De Cesare N., Galli C., Salvioni A., Tramontana C., Tamborini G., Bartorelli A. Calcium-channel blockade with nifedipine and angiotensin converting-enzyme inhibition with captopril in the therapy of patients with severe primary hypertension. Circulation. 1984 Aug;70(2):279–284. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber M. E., Brigden G. S., Caruana M. P., Lahiri A., Raftery E. B. First dose response and 24-hour antihypertensive efficacy of the new once-daily angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Aug 1;62(4):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landahl S., Edgar B., Gabrielsson M., Larsson M., Lernfelt B., Lundborg P., Regårdh C. G. Pharmacokinetics and blood pressure effects of felodipine in elderly hypertensive patients. A comparison with young healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Jun;14(6):374–383. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814060-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees K. R., Reid J. L. Lisinopril and nifedipine: no acute interaction in normotensives. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;25(3):307–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liedholm H., Melander A. A placebo-controlled dose-response study of felodipine extended release in hypertensive patients. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;14(1):109–113. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198907000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. K., Clements J. A. Simplified radioimmunoassay for serum aldosterone utilizing increased antibody specificity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):622–627. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith P. A., Elliott H. L., McSharry D. R., Kelman A. W., Reid J. L. The pharmacokinetics of endralazine in essential hypertensives and in normotensive subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;16(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. R., Gobel F. L., Jorgensen C. R., Wang K., Wang Y., Taylor H. L. Hemodynamic predictors of myocardial oxygen consumption during static and dynamic exercise. Circulation. 1974 Dec;50(6):1179–1189. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.50.6.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. R., Wilkins M. R., Jack D. B., Kendall M. J., Laugher S. Pharmacokinetic interactions between felodipine and metoprolol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;31(5):575–578. doi: 10.1007/BF00606633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struthers A. D., Pai S., Seidelin P. H., Coutie W. J., Morton J. J. Evidence in humans for a postsynaptic interaction between noradrenaline and angiotensin II with regard to systolic but not diastolic blood pressure. J Hypertens. 1987 Dec;5(6):671–676. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198712000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Kumagai Y., Tateishi T., Seguchi H., Ebihara A. Effects on autonomic function of a new angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 3):S40–S44. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900133-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


