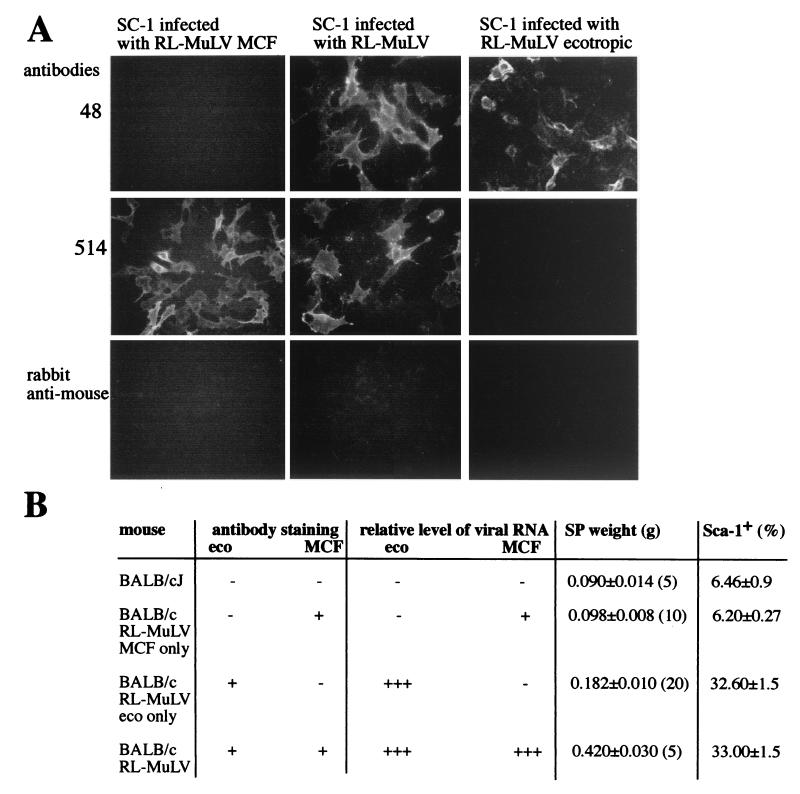
FIG. 5.
The ecotropic virus, but not the MCF virus, component of the RL-MuLV mixture causes splenomegaly. (A) Harvests from RL-MuLV-infected SC-1 cells were passaged six times in mink lung cells. After the sixth passage, harvests were used to infect SC-1 cells. Infected SC-1 cells were passaged and then stained with MAbs 48 and 514 followed by FITC-labeled polyclonal rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulins. Similarly, harvests from RL-MuLV-infected SC-1 cells were passaged five times in XC cells, followed by infection of SC-1 cells. Also shown is the staining of infected RL-MuLV-infected SC-1 cells. (B) Harvests of the RL-MuLV ecotropic virus and MCF virus components were tested for the ability to cause disease in BALB/cJ mice. Harvest of SC-1 vir6-infected cells was used as a control. Four-week-old mice were injected with harvests from vir6-infected, MCF virus-infected, or ecotropic virus-infected SC-1 cells. Three months after infection, mice were sacrificed, spleen weights were recorded, and RNA isolated from a portion of the spleen was subjected to Northern blot analysis with ecotropic virus- and MCF virus-specific probes. +++, +, and −, relative levels of viral RNA detected in spleens by Northern blot analysis. A single-cell suspension isolated from another portion of the spleen was stained with anti-Sca-1 MAb and analyzed by FACS. Splenic cells were also cocultured with SC-1 cells. On day 5, infected SC-1 cells were stained with MAbs 514 and 48. + and −, positive and negative staining with MAbs. Numbers in parentheses, numbers of mice used. For the infection studies, 8,000 XC PFU of vir6 and ecotropic virus and 8,000 UV-mink PFU of MCF virus were used.