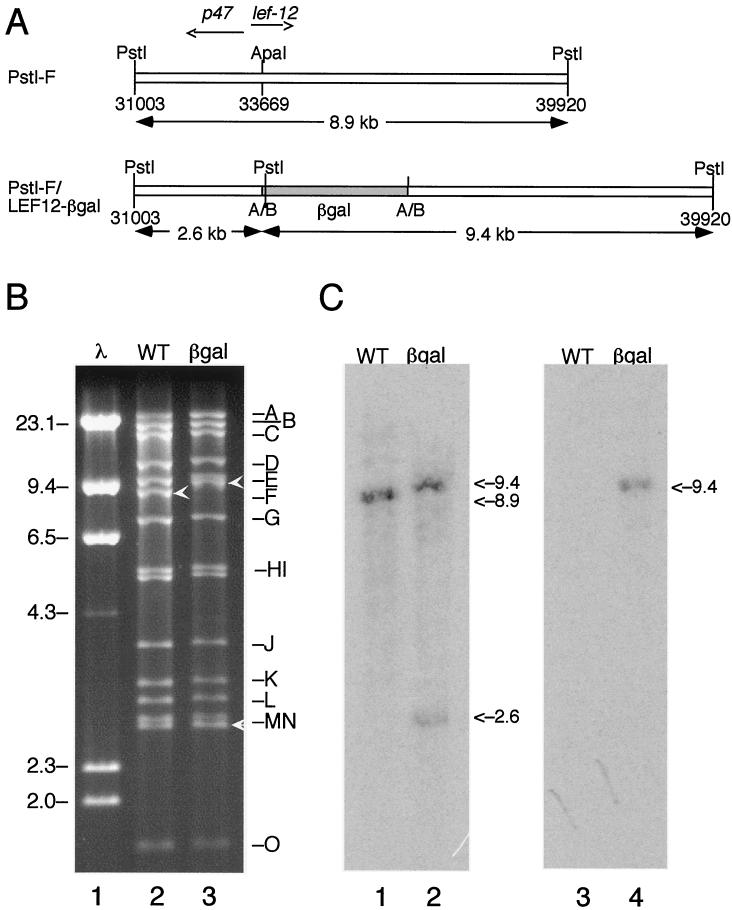
FIG. 1.
Construction of vLEF12-βgal. (A) Strategy. The recombinant virus vLEF12-βgal encodes the first 96 amino acids of LEF-12 fused in frame with β-galactosidase. This virus was constructed by in vivo recombination between wild-type viral DNA and a plasmid containing the β-galactosidase gene (shaded) inserted into an ApaI site within the open reading frame of lef-12. This virus was selected as a blue plaque recombinant when plated in the presence of X-Gal. The positions of the ApaI sites converted to BglII sites are indicated by A/B. The genome positions of the PstI and ApaI sites are indicated. (B) Restriction enzyme digest. DNA purified from wild-type virus (lane 2) and vLEF12-βgal virus (lane 3) was digested with PstI, and fragments were separated on a 0.8% agarose gel. Lambda DNA digested with HindIII was run in an adjacent lane as molecular size markers (lane 1). The locations of the genomic fragments are indicated on the right, and the sizes of the relevant lambda markers are indicated on the left (in kilobases). The PstI-F fragment in wild-type virus and the two PstI-F subfragments in the mutant virus are indicated by white arrowheads. (C) Southern blot. Duplicate sets of digests were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and separately probed with uniformly radiolabeled PstI-F genomic DNA fragment (lanes 1 and 2) and β-galactosidase DNA (lanes 3 and 4).