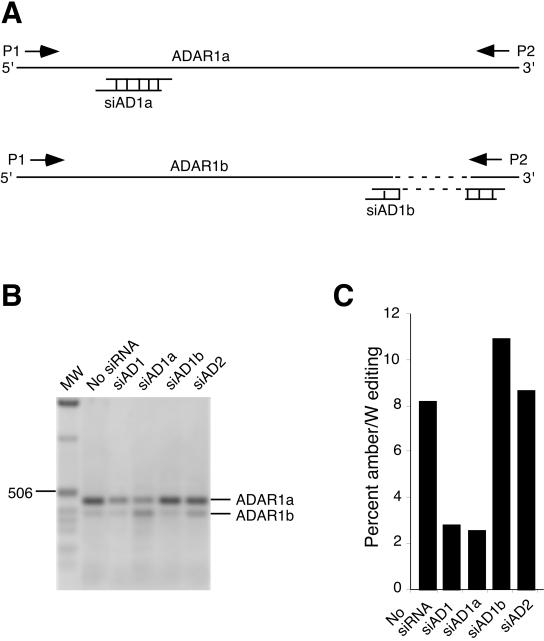
FIG. 2.
Effects of ADAR1 splice variants on HDV amber/W editing. (A) Illustration of the structure of ADAR1 splice variants ADAR1a and ADAR1b (24). ADAR1b is generated by alternative splicing at exon 7 and has a deletion of 78 nucleotides (shown by the dashed line) compared with ADAR1a. Locations of primers P1 and P2 used for RT-PCR analysis of ADAR1a and ADAR1b expression are indicated by leftward and rightward arrows. Locations of ADAR1a- and ADAR1b-specific siRNAs are indicated schematically. Note that the sketch is not drawn to scale. (B) RT-PCR analyses to detect the efficiency of ADAR gene targeting by siRNAs. Huh-7 cells were transfected with siAD1, siAD1a, siAD1b, or siAD2, as in Fig. 1. RNAs were harvested 4 days posttransfection and analyzed by RT-PCR. Products were run on 1% agarose gels, stained with ethidium bromide, and photographed. The image shown is an inverted image of a scanned photograph, which better illustrates the reduction of intensity of several bands. MW, molecular weight standards (1-kb ladder; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.). Sizes of selected molecular weight markers are indicated, as are the locations of the predicted RT-PCR products for ADAR1a and ADAR1b. (C) Effect of siRNA-targeted reduction of ADAR1a and ADAR1b on HDV amber/W editing. Huh-7 cells were transfected with pHDV · I(+) and the indicated siRNAs; RNAs were harvested 6 days posttransfection and analyzed for HDV amber/W editing as in Fig. 1.