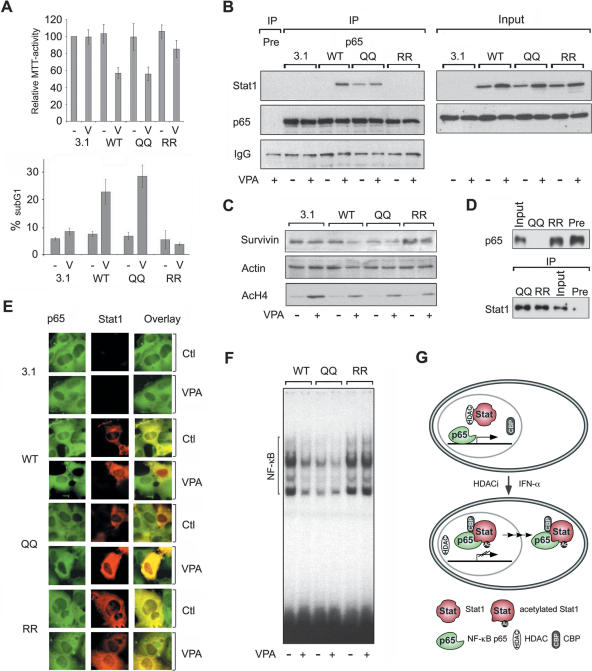
Figure 7.
Identification of Stat1α acetylation as critical regulator of HDACi-induced apoptosis. (A) NW-1539 cells were transfected with Stat1α (WT, wild type), lysine mutants, or equal amounts of empty vector (pc3.1). Proliferation and apoptosis were scored 72 h later by MTT and PI FACS analysis, respectively. (WT) Wild type; (QQ) 410,413K → Q; (RR) 410,413K → R; (–) untreated; (V) 1.5 mM VPA. (B) Interaction of overexpressed wild-type (WT) and mutant Stat1α (QQ, RR) with NF-κB p65 in U3A cells was analyzed by IP and Western blot. Cells were incubated with 1.5 mM VPA for 48 h or left untreated. Input lanes are 2% of the lysate used for IP and are shown at expositons allowing signal comparison. (C) U3A cells were transfected and treated as described in B. Survivin expression was analyzed by Western blot. Detection of actin and AcH4 serve as loading and treatment controls, respectively. (D) SK-37 nuclear lysates were incubated with HA-Stat1 (QQ, 410,413K → Q; RR, 410,413K → R) immunoprecipitated in RIPA buffer or a precipitate formed with a control antibody (pre). Ten microliters of input and 20 μL of depleted nuclear extract were loaded (upper panel). The lower panel shows equal Stat1 IP efficiencies. (E) NF-κB p65 localization was analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy of NW-1539 cells transfected and treated as described in B. Note: Compare transfected and nontransfected cells within each field. (F) DNA binding of NF-κB was investigated by EMSA with cell lysates of NW-1539 cells transfected and treated as described in B. (G) Model for acetylation-dependent Stat1–NF-κB cross-talk.