Figure 1.
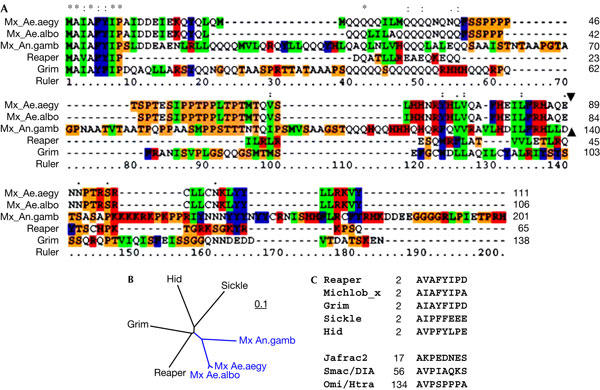
Comparison of Mx sequences with Reaper and Grim. (A) Alignment of Mx sequences from Anopheles gambiae (An.gamb), Aedes albopictus (Ae.albo) and Aedes aegypti (Ae.aegy), and Grim (NP_524137) and Reaper (NP_524138) sequences from the fruitfly. The relative position of the single intron (indicated with solid triangle) in mx genes is conserved between Anopheles and Aedes. There are no introns in grim or reaper. The colour scheme reflects percentage identity among the five aligned sequences (red, 100%; blue, >75%; and green, >50%). (B) Protein distance tree showing that Mx is slightly closer to Reaper and Grim than to Hid and Sickle. The scale bar reflects the rate of nucleotide change per position. (C) Comparison of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP)-binding motifs in fly (Reaper, Grim, Hid (NP_524136), Sickle (NP_524139) and Jafrac2 (Q9V3Q4)), mosquito (Michlob_x) and human (Smac/IDIA (NP_063940), OmiI/HtrA (O43464)) IAP antagonists. Numbers indicate the position of the first Ala in the host proteins.
