Figure 3.
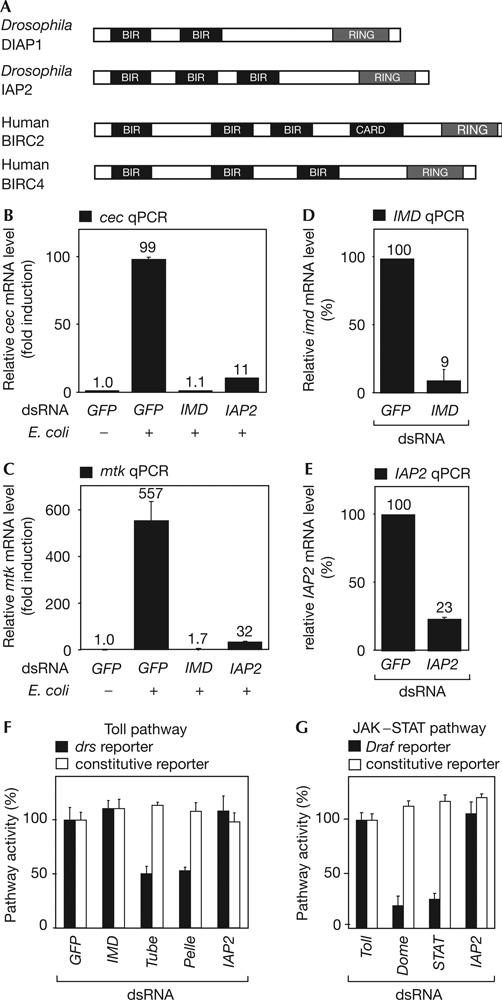
Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein 2 is specifically required for immune deficiency signalling. (A) Domain structure of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein 2 (IAP2). Drosophila proteins DIAP1 and IAP2 and two human IAPs, BIRC2 (BIR-containing protein 2) and BIRC4 are depicted. Two or three BIR motifs located close to the amino terminus are characteristic features of all IAPs. (B,C) Quantitative real-time reverse transcription–PCR (qPCR) experiments monitoring the effect of IAP2 RNA interference (RNAi) on endogenous immune deficiency (IMD)–Rel target gene induction after an immune stimulus. The messenger RNA levels of the IMD–Rel target genes cecropinA2 (cec) and Metchnikowin (Mtk) are induced 99- and 557-fold in response to bacterial induction, respectively (GFP, +). Depletion of IMD by RNAi inhibits induction of cec and mtk expression (IMD, +). Similarly, IAP2 RNAi significantly reduces expression of both peptides in response to a bacterial challenge (IAP2, +). (D,E) IMD and IAP2 levels are strongly reduced by the corresponding doublestranded RNA (dsRNA). (F) Test for requirement of IAP2 in the Toll pathway in SL2 cells. Toll signalling is reduced when components of the Toll pathway are knocked down by RNAi (Tube, Pelle). Depletion of unrelated factors (GFP), components of the IMD pathway (IMD) or IAP2 does not affect Toll signalling activity (black bars, Drosomycin reporter). (G) Test of IAP2 activity in the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) pathway in S2R+ cells. JAK–STAT signalling is disturbed when components of the JAK–STAT cascade are depleted by RNAi (Dome, STAT92E; black bars, 2x6xDraf luc reporter). Signalling is not blocked when unrelated factors (Toll) or IAP2 are knocked down by RNAi (IAP2). Error bars represent standard deviation of three independent replicates.
