Figure 2.
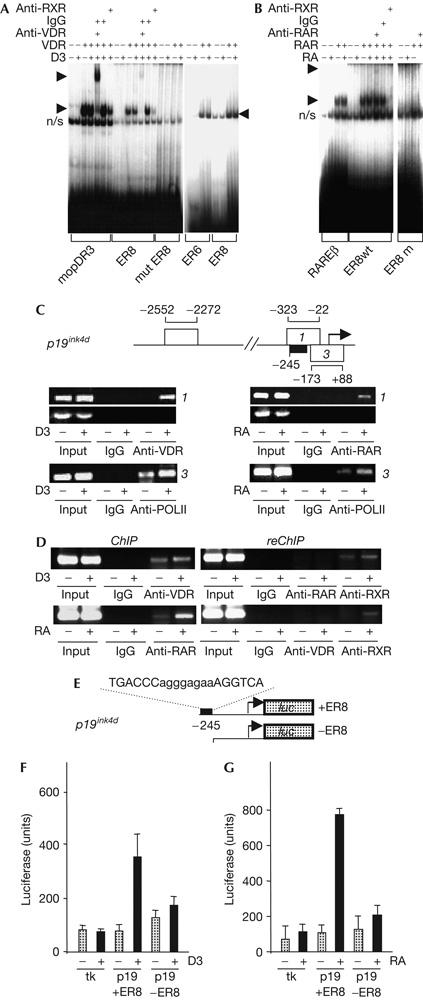
Characterization of in vitro and in vivo p19ink4d ER8 element function. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) of binding of vitamin D receptors (VDRs)/retinoid X receptors (RXRs) to the p19ink4d ER8, with binding to the mouse osteopontin (mop) DR3 vitamin D responsive element as a control, along with a comparison of binding to ER6 and ER8 motifs (right-hand panel). (B) EMSA of retinoic acid receptor (RAR)/RXR binding to the p19ink4d ER8, and the rarβ DR5 retinoic acid response element, as a control. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of binding of VDRs and RARs to the p19ink4d ER8 (region 1) and RNA polymerase II (POLII) binding to the transcription start site. (D) ReChIP analysis confirms the presence of VDR/RXRs and RAR/RXRs but not of VDR/RARs on the p19ink4d ER8. (E) Cloning of p19ink4d promoter containing or lacking ER8 upstream of a luciferase reporter. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25D3)- (F) and retinoic acid (RA)-regulated (G) luciferase expression is dependent on the ER8 element in the p19ink4d promoter. Luciferase expression driven by a thymidine kinase (tk) control promoter is shown.
