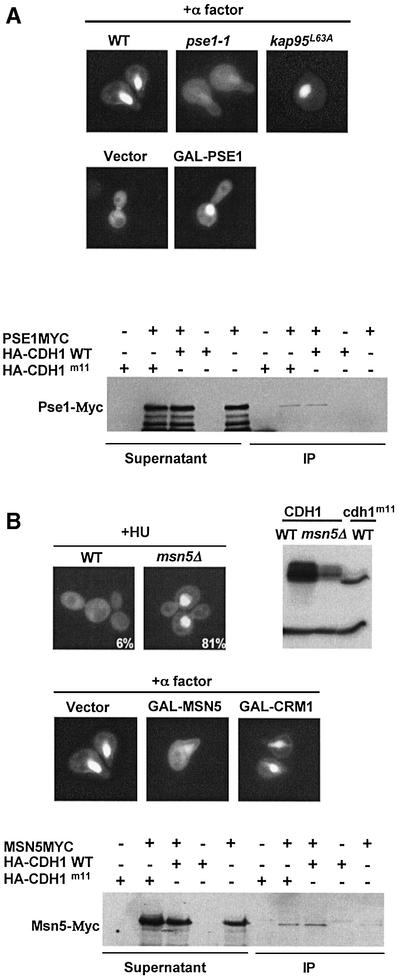
Fig. 3. The nuclear localization of Cdh1p is controlled by the importin Pse1p and the exportin Msn5p. (A) Wild-type (K699) cells or temperature-sensitive mutants in the import receptors Pse1p (pse1-1, YBL1) or Kap95p (kap95L63A, YBL14) were arrested in G1 by α-factor, and the localization of Cdh1p–GFP was analysed by GFP microscopy (upper panel). Note that nuclear accumulation of Cdh1p–GFP requires functional Pse1p. Overexpression of Pse1p from the inducible GAL promoter was sufficient for nuclear accumulation of Cdh1p–GFP (middle panels) at cell cycle stages where Cdh1p is predominantly cytoplasmic (vector). Pse1p-myc was able to co-immunoprecipitate (IP) with both wild-type HA3-Cdh1p and unphosphorylatable Cdh1p-m11-HA (lower panel). For co-immunoprecipitation, extracts prepared from cells expressing Pse1p-myc and, as indicated, either no protein (vector), wild-type HA3-Cdh1p or non-phosphorylatable HA3-Cdh1p-m11 were incubated with HA11 antibodies. The immunoprecipitates (IP) were analysed by immunoblot analysis with anti-Myc antibodies (9E10). For control, an aliquot of the extracts before immunoprecipitation (supernatant) was included. (B) The localization of Cdh1p–GFP was examined in wild-type (K699) and msn5Δ (YMJ1171) cells arrested with HU. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells with nuclear accumulation of Cdh1p–GFP; at least 200 cells were included in the analysis. The phosphorylation state of HA-Cdh1p and HA3-Cdh1p-m11 was analysed by immunoblotting in wild-type and msn5Δ cells as indicated (right blot). Overexpression of the exportin Msn5p but not Crm1p from the inducible GAL promoter in wild-type cells arrested with α-factor was sufficient to promote nuclear export of Cdh1p–GFP (middle panel). Co-immunoprecipitation experiments between Msn5p-myc and Cdh1p (lower panel) were performed as described in (A).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.