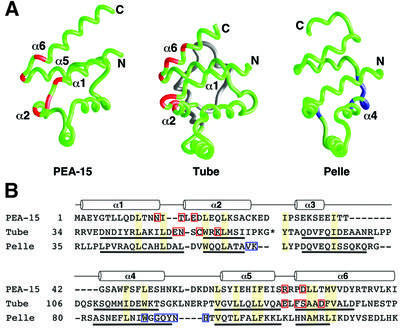
Fig. 6. Comparison of the PEA-15 DED, Tube DD and Pelle DD binding epitopes. (A) Backbone representations of the death motifs of PEA-15, Tube and Pelle (Xiao et al., 1999; PDB accession code 1D2Z) with residues important for binding their target proteins highlighted in red for PEA-15 and Tube and in blue for Pelle. Tube contains an insertion of two short α-helices between helices α2 and α3 (shown in gray) that is not part of the core structure of the DD. (B) Structure-based sequence alignment of mouse PEA-15, Drosophila melanogaster Tube DD and D.melanogaster Pelle DD created from pairwise superpositions calculated in DALI (Holm and Sander, 1993). The positions of helices are indicated by cylinders for PEA-15, and the helices for Tube and Pelle are underlined. Conserved residues which form part of the hydrophobic core in each protein are shaded yellow. The asterisk in the Tube sequence indicates a two-helix insertion (Xiao et al., 1999) that has been omitted for clarity. Sites corresponding to mutations that are deleterious to function are highlighted with red boxes for PEA-15 (this study). Interfacial residues observed in the Tube–Pelle DD complex structure are indicated by red boxes for Tube DD and blue boxes for Pelle DD (Xiao et al., 1999).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.