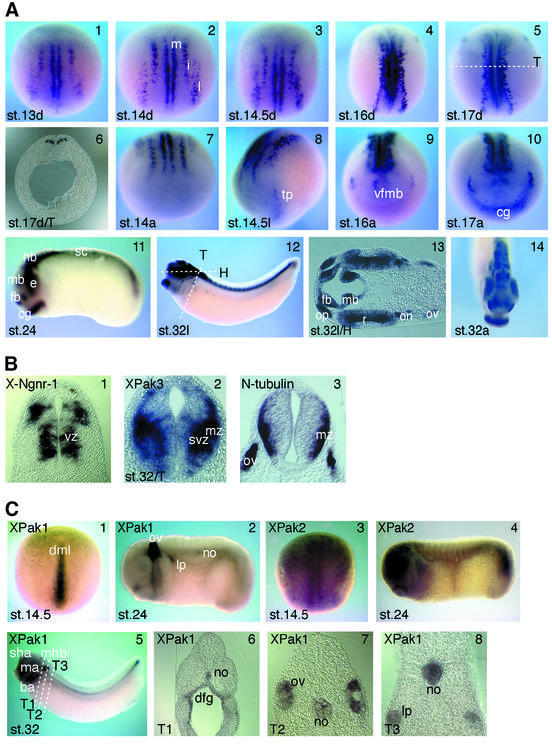
Fig. 2. Differential expression patterns of XPak genes during Xenopus development. (A) Spatial and temporal expression of XPak3 was analysed at different stages (st.) of neurogenesis using whole-mount in situ hybridization. (1–5) XPak3 transcripts are found in three bilateral stripes, lateral (l), intermediate (i) and medial (m), in the posterior neural plate. Embryos are shown in a dorsal (d) view with anterior up. (6) In a transverse (T) section of a stage 17 embryo at the level shown in panel 5 (white dotted line), XPak3 transcripts are detectable in the deep layer of the neuroectoderm in regions corresponding to the medial, intermediate and lateral stripes. Panels 7–10 show the expression in the anterior neural plate; (8) XPak3-expressing cells first appear in the trigeminal placode (tp), then (9) in a centrally located, semicircular array corresponding to a ventral area within the prospective fore-/midbrain where neurons first develop (vfmb) and (10) in the cement gland (cg). (11–14) At later stages of neurogenesis, XPak3 is expressed in the forebrain (fb), midbrain (mb), hindbrain (hb), retina (r), optic nerve (on), olfactory placode (op), otic vesicle (ov) and cement gland (cg): (11 and 12) lateral view (l), (13) horizontal (H) section of the head region at the level indicated in panel 12, (14) anterior view (a). (B) Differential expression of neuronal marker genes in the neural tube of stage 32 embryos. (1) X-Ngnr-1 is expressed in the ventricular zone (vz), (3) N-tubulin in the marginal zone (mz) and (2) XPak3 in the marginal and subventricular zone (svz). The level of the transverse (T) sections is shown in (A) panel 12. (C) Expression patterns of XPak1 and XPak2. (1) XPak1 transcripts are present in the dorsal midline (dml) and (2 and 5–8) later in the otic vesicle, mandibular arch (ma), branchial arch (ba), midbrain–hindbrain boundary (mhb), stomodeal–hypophyseal anlage (sha), lateral placode (lp), notochord (no) and dorsal foregut (dfg). (3) Early on, XPak2 is expressed ubiquitously in the neural plate and (4) later the expression becomes stronger in the brain, eye and tailbud. Embryos are shown in (1 and 3) dorsal view with anterior up and (2, 4 and 5) lateral view. (6–8) Levels of the transverse (T) sections (T1–3) are indicated in panel 5.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.