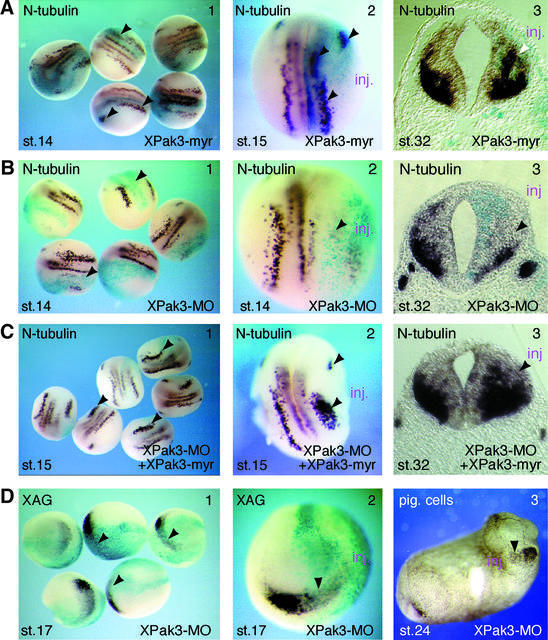
Fig. 4. XPak3 activation induces premature neuronal differentiation. (A–C) Modulation of XPak3 activity influences neuronal differentiation. Xenopus albino embryos were injected into one blastomere at the two-cell stage with (A) 10 pg of XPak3-myr RNA, (B) 2.5 pmol of XPak3-MO and (C) 2.5 pmol of XPak3-MO/12.5 pg XPak3-myr RNA, all with LacZ RNA as tracer. Embryos were fixed at neurula and tailbud stages, then stained with X-gal (light blue) and analysed for neuronal differentiation, as marked by N-tubulin expression. (A3, B3 and C3) Transverse sections of stage 32 embryos were prepared at the level of the hindbrain. (A1 and 2) XPak3-myr injection results in increased N-tubulin expression within the trigeminal placode and within the territories of primary neurons, as indicated by arrowheads (71%, n = 46). (A3) In the neural tube, XPak3-myr injections expand/shift the expression domain of N-tubulin from the marginal zone towards the ventricular zone (white arrowhead). (B1–3) XPak3-MO injections strongly inhibit N-tubulin expression within both the trigeminal placode and the territories of primary neurons (100%, n = 92), and within the neural tube. (C1 and 2) Co-injection of XPak3-MO and XPak3-myr RNA results in rescue of N-tubulin expression in a pattern that is not identical to, but reminiscent of the normal one (84%, n = 73). (C3) In the neural tube, co-injection increases/expands the expression domain of N-tubulin similarly to XPak3-myr injection (see A, panel 3). (D) XPak3 is necessary for cement gland formation. Embryos were injected into one blastomere of two-cell stage embryos with 2.5 pmol of XPak3-MO and LacZ RNA as tracer. One batch of these embryos was fixed at stage 17, stained for β-galactosidase activity (light blue) and bleached. The other batch was fixed at stage 24. (1 and 2) By whole-mount in situ hybridization, XAG is found to be suppressed, as marked by arrowheads (100%, n = 71). (3) In stage 24 embryos, pigmented cement gland cells are missing on the injected side.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.