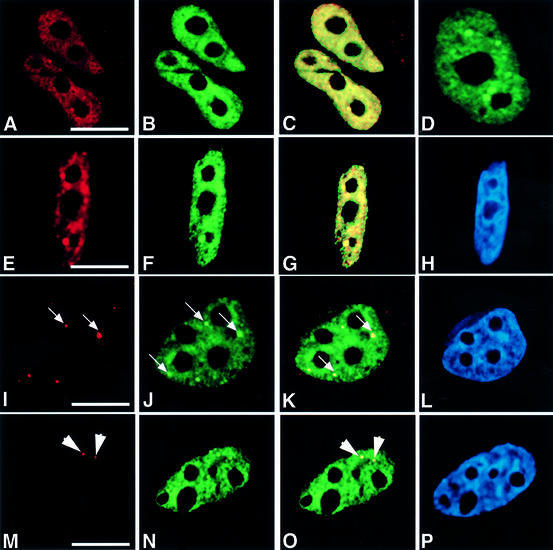
Fig. 1. HCF-1 co-localizes with nuclear structures that contain pre-mRNA splicing factors. HeLa cells were transfected with pEYFP-HCF, and indirect immunofluorescence experiments were performed on the transfected cells using various antibodies. The arrows point to gems, while the arrowheads point to Cajal bodies. (A) Light microscopic image of an indirect immunofluorescence experiment on HeLa cells using the polyclonal HC2 antibody. (B) A microscopic image obtained from the direct fluorescence of YFP–HCF-1 in the same cells as in (A). (C) Superimposed optical sections from (A) and (B). Co-localization of green and red results in the yellow colour. Note the presence of some green fluorescence that does not co-localize with the antibody staining. This may be due to the stronger fluorescence signal produced by the YFP–HCF-1 fusion protein. Secondly, YFP–HCF-1/cellular HCF-1 may exist in some complexes that, although visible by direct YFP fluorescence, are inaccessible to the anti-HCF-1 peptide antibodies used for cell staining. (D) Light microscopic image of a live HeLa cell expressing YFP–HCF-1 (green). (E, I and M) Microscopic images of indirect immunofluorescence experiments on HeLa cells using anti-Sm antibody (Y12), anti-SMN mAb (MANSMA1) and anti-p80 coilin mAb (5P10), respectively. (F, J and N) Microscopic images obtained from the direct fluorescence of YFP–HCF-1 in the same cells as in (E), (I) and (M), respectively. (G, K and O) Superimposed optical sections from (E) and (F), (I) and (J), and (M) and (N), respectively. (H, L and P) Microscopic images obtained from DAPI staining of the HeLa cells shown in (E), (I) and (M), respectively. Bar = 5 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.