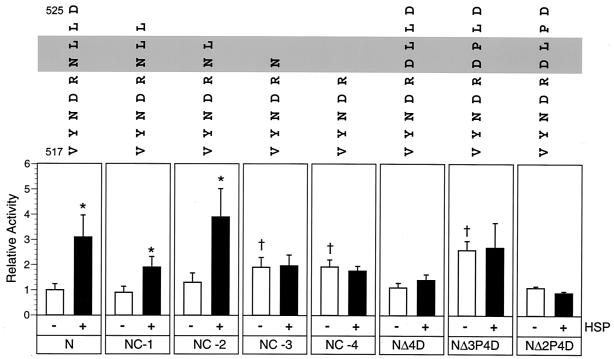
FIG. 3.
Hsp72-dependent stimulation of MV minireplicon CAT reporter gene expression when N protein or N protein mutants provide the template function. Cell monolayers were transfected in triplicate with plasmids directing the expression of minigenomic RNA and transcripts for P, L, parental N, and mutant N proteins. The N protein mutants included C-terminal truncations or amino acid substitutions representing naturally occurring sequence polymorphisms. Truncated proteins lacked the last one (NC-1), two (NC-2), three (NC-3), or four (NC-4) amino acids. Amino acid substitutions replaced the asparagine at amino acid 522 of the N protein with aspartic acid (NΔ4D). The NΔ3P4D and NΔ2P4D mutants contained an additional leucine-to-proline substitution at amino acids 523 and 524, respectively. Hsp72 supplementation was done by adding either 1.0 or 2.5 μg of pT7VSV-Hsp72 per transfection. Cell extracts were processed separately for measurement of CAT activity; results are expressed as an experimental average with correction for transfection efficiency, and that value was averaged for three separate but consecutive trials. The mean and standard error of the mean are presented relative to the activity supported by parental N protein, where the latter equals 1.0. The Hsp72 supplementation level yielding the greatest stimulation of reporter gene expression (black bars) was compared to results for treatment groups lacking Hsp72 supplementation (white bars). Western blot analyses showed constant levels of N antigen expression between treatment groups when those levels were adjusted for transfection efficiency (data not shown). Significant differences in reporter gene expression in Hsp72-supplemented versus nonsupplemented reactions were identified by using Student's t test (P < 0.05) and are indicated by an asterisk. Similarly, significant differences between basal activities supported by mutant N protein and parental N protein are indicated by a dagger. The C-terminal sequence of each N construct is indicated above the corresponding histogram, beginning at amino acid 517. Amino acids 522 to 523 (grey) significantly influence either basal or Hsp72-dependent minireplicon reporter gene expression.