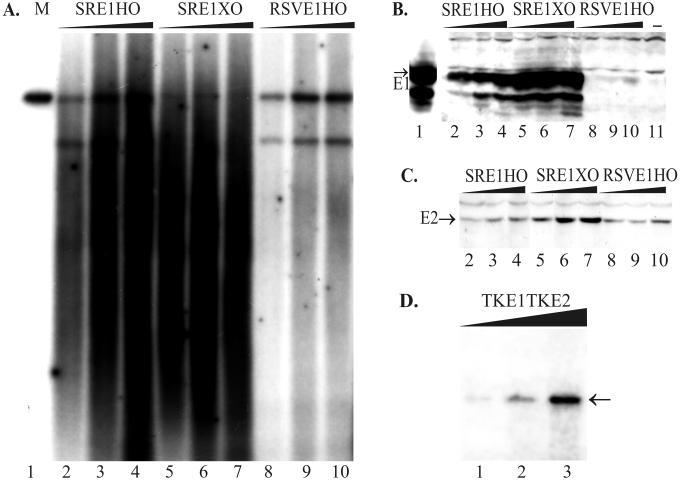
FIG. 2.
The replication properties of the designed plasmids are dependent on E1 protein expression. (A and D) A transient-replication assay was carried out with plasmids with promoters of different strengths for E1 in CHO cells. Increasing amounts of plasmid DNA (1, 2, and 5 μg) were transfected by electroporation into CHO cells, and episomal DNA was extracted 72 h later. (A) Purified episomal DNA was digested using linearizing enzymes EcoRI (lanes 2 to 4) or HindIII (lanes 5 to 10 [also panel D]) together with DpnI. Two hundred picograms of linear DNA (SRE1HO) was used as a marker on the blot (lane 1). X-ray film was exposed for 24 h (A) or 48 h (D). The position of unit-sized plasmid is indicated by the arrow (D). (B) Western blot analysis for E1 protein expression from transfected CHO cells. In this experiment, the strong SRα promoter was driving E1 expression in the case of plasmids SRE1HO and SRE1XO, which differ from each other in ori location in the plasmid (lanes 2 to 4 and 5 to 7, respectively). The weaker RSV promoter was driving E1 expression in the plasmid RSVE1HO (lanes 8 to 10). As a marker, the lysate from the COS7 cells, transfected with 0.5 μg of E1 expression construct pCGEag, was used as a positive control (lane 1), and only carrier DNA-transfected CHO cells were used as the negative control (lane 11). (C) Western blot analysis for E2 expression directed by the MoMuLV LTR from the plasmids SRE1HO (lanes 2 to 4), SRE1XO (lanes 5 to 7), and RSVE1HO (lanes 8 to 10).