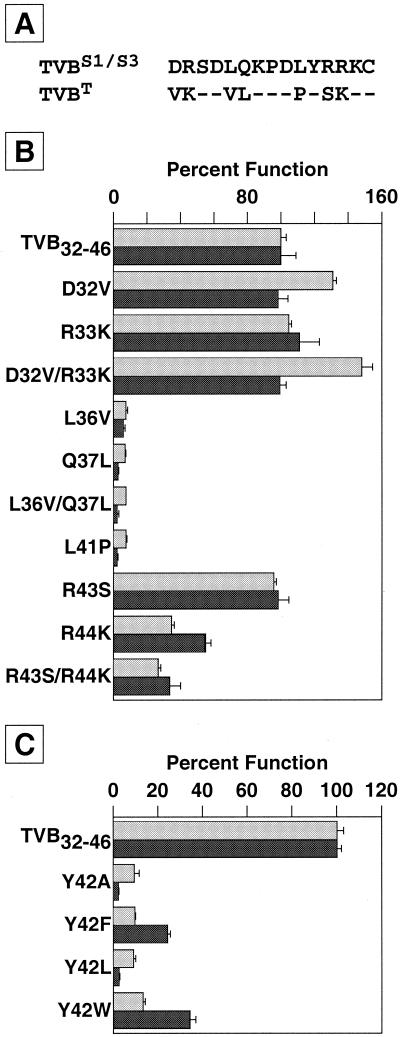
FIG. 3.
Identification of four functionally important residues of TVB32-46. (A) The amino acid sequences of the chicken TVBS1 and TVBS3 receptors and of the turkey TVBT protein are shown aligned over the region represented by TVB32-46. Dashes represent conserved residues. (B) Residues Leu-36, Gln-37, and Leu-41 are important for TVB32-46 function. A set of altered biotinylated peptides was generated in which residues that were specific to TVBT were used to replace the corresponding residues in the TVB32-46 peptide. These altered peptides were tested for binding to SUB-rIgG (light shaded bars) and for the ability to mediate viral infection (dark shaded bars) as described in the legends to Fig. 1B and C and Fig. 2. (C) Residue Tyr-42 is important for TVB32-46 function. An additional set of peptides was also synthesized in which residue Tyr-42 was replaced with other amino acids, and these peptides were tested as in the experiment for which results are shown in panel B. In panels B and C, 100% infection represents a multiplicity of infection of 0.36 (B) or 0.6 (C) GFP-transducing units (measured from the level of infection achieved in the presence of the wild-type TVB32-46 peptide). Data are means and standard deviations (error bars) from at least three independent experiments that were performed in triplicate.