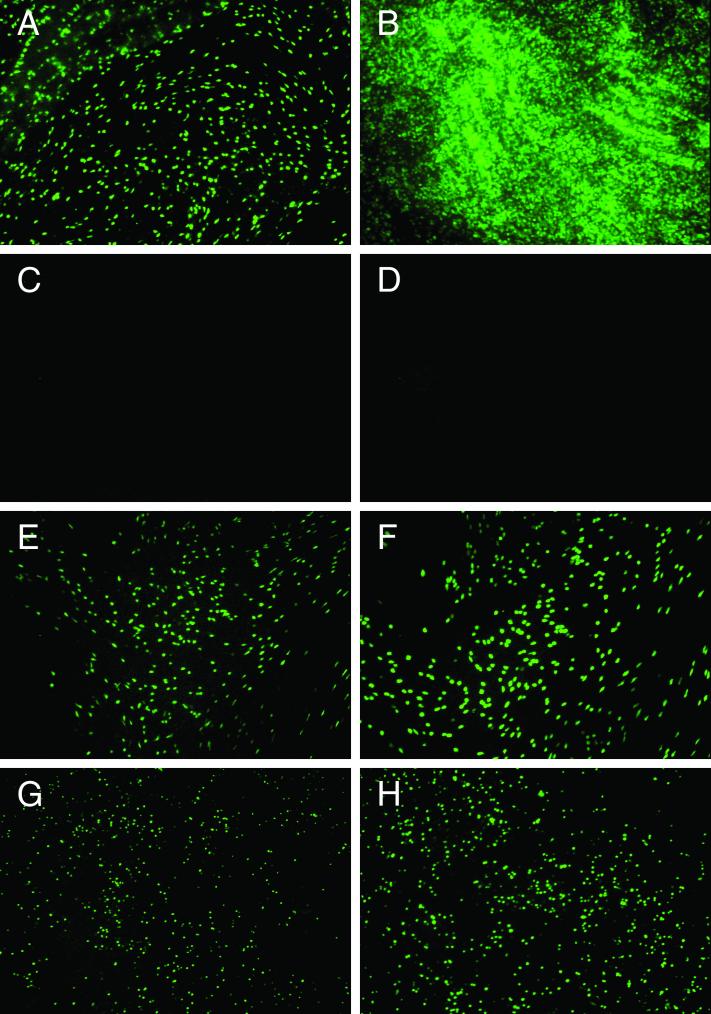
FIG. 8.
Inhibition of initial rgRSV infection and spread in WD HAE cultures with an RSV-neutralizing monoclonal antibody or ribavirin. The apical surfaces of HAE cultures were inoculated with rgRSV (105 PFU; MOI, ∼0.3), and GFP expression was monitored en face by fluorescence photomicroscopy 1 (A) and 3 (B) days later. To assess the effects of potential RSV inhibitors on initial rgRSV infection, parallel cultures were treated prior to rgRSV inoculation with either 250 μg of the F-specific RSV-neutralizing monoclonal antibody Synagis/ml applied to the apical surface (C) or 100 μg of ribavirin/ml included in the basolateral medium (D). The cultures were then inoculated with rgRSV as described above, and GFP expression was assessed 1 day later by fluorescence photomicroscopy. To assess the effects of RSV inhibitors on viral spread, parallel cultures were inoculated as described above and then treated with Synagis 6 h postinoculation, and GFP expression was assessed on day 1 (E) and day 3 (F) postinoculation. Cultures treated with ribavirin 24 h postinoculation were assessed for GFP expression by fluorescence photomicroscopy on day 2 (G) and day 4 (H) postinoculation. Original magnification, ×10.