FIG. 2.
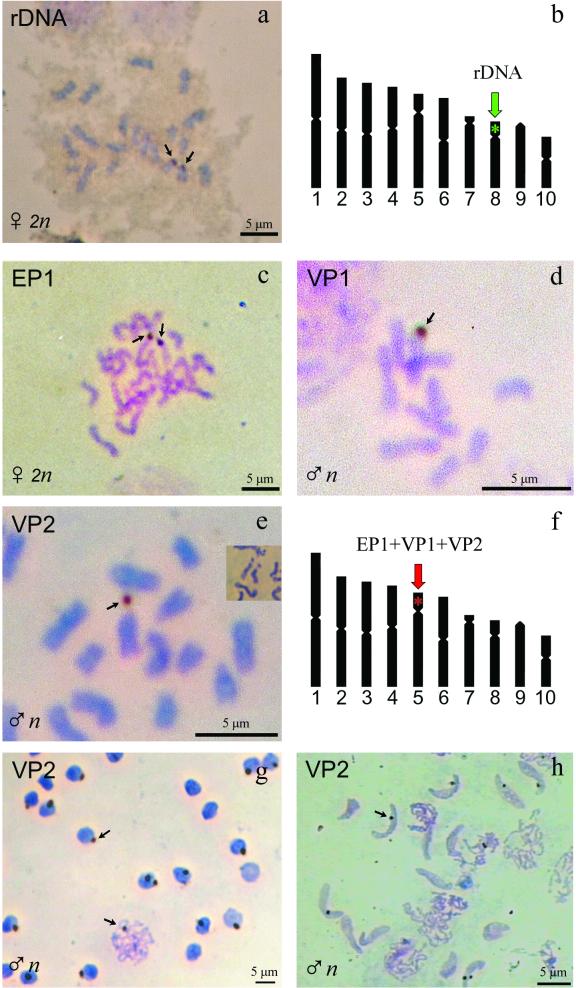
(a) In situ hybridization of C. congregata chromosomes with the rDNA probe in developing brain of prepupal stage wasps. (b) Summary of the results, showing that the location of hybridization (arrows) corresponds to the short arm of chromosome 8. (c, d, and e) In situ hybridization of C. congregata chromosomes with the C. congregata PDV probes EP1, VP1, and VP2, respectively, corresponding to different virus segments. Developing brain cells were used in panels c and e, and developing gonads were analyzed in panel d. In panel e, the inset shows that the primary constriction of chromosome 5 can be elastic, so that the dot-shaped arm of chromosome 5 occasionally appears as separated from the centromere, as in the VP2 hybridization picture. (f) Summary of the results, showing that the location of hybridization (arrows) is common to all the virus sequences used as probes and corresponds to the short arm of chromosome 5 (red star). (g) Hybridization of the VP2 probe on interphase nuclei and on meiotic chromosomes from haploid male cells. (h) Hybridization of the same VP2 probe on chromosomal DNA in nuclei from spermatids, where the virus sequences appear to have a common location within the condensed chromatin.