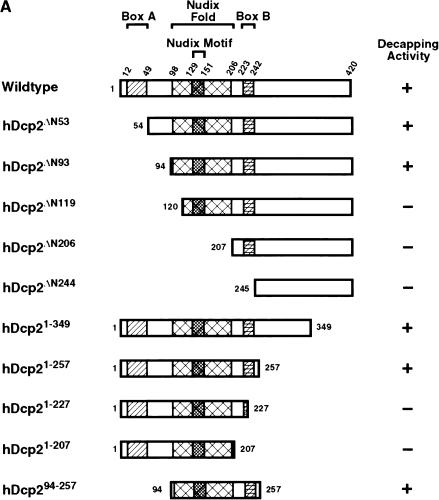
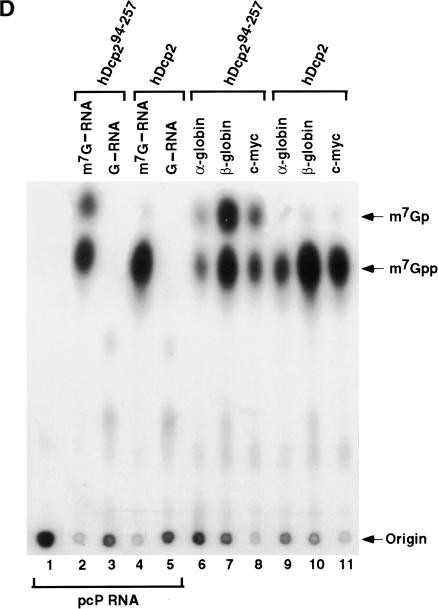
FIGURE 2.
Identification of a minimal hDcp2 domain sufficient for cap hydrolysis. (A) The hDcp2 protein and the various truncation proteins are shown schematically. The three regions highly conserved in hDcp2 from diverse organisms are denoted as the 37 amino acid Box A, the 109 amino acid Nudix fold with the central 23 amino acid Nudix motif, and the 19 amino acid Box B segment. The numbers above and on either side of the schematic diagrams represent amino acid positions. The decapping activity for each protein is summarized at right by a + or − for those that can and cannot decap, respectively. (B) Purified recombinant protein was resolved on a 12.5% SDS-PAGE and detected with Coomassie blue. (C) Decapping assays of hDcp2 and hDcp2 mutant proteins. The assays were carried out using 20 pmoles of each protein with cap-labeled pcP-G16 substrate, and the reaction products were resolved by TLC. The quantitation for the decapping efficiency of each protein is presented as the percentage decapping using ImageQuant 5.2 software. Migration of the standards are shown at right. (D) The minimal hDcp294–257 protein retains methyl cap specificity and efficiently utilizes different RNA substrates. Decapping assays were carried out as described above using the 3′ UTR sequences of the indicated mRNAs (α-globin, β-globin, c-myc) and pcP. N-7 methyl-containing capped pcP RNA is denoted as m7G—RNA, whereas the unmethylated is represented as G—RNA. Migration of the standards are indicated on the right.