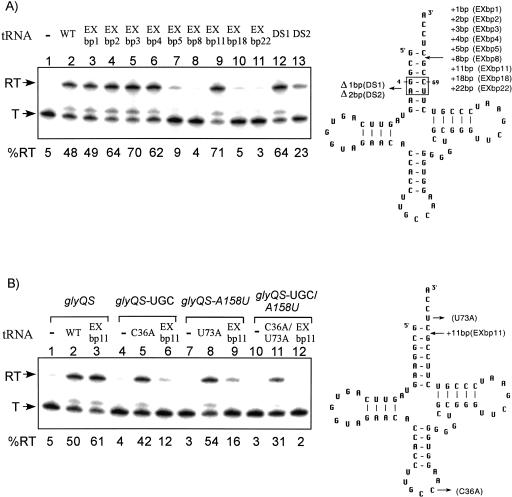
FIGURE 3.
Effects of tRNAGly acceptor stem insertions and deletions. (Left) The in vitro transcription of glyQS templates; (right) the cloverleaf models of B. subtilis tRNAGly variants. (T) terminated transcript; (RT) readthrough transcript; (WT) wild-type tRNAGly. Percent readthrough is indicated at the bottom of each lane. Arrows indicate positions of substituted, added (+), or deleted (Δ) residues or base pairs. (A) Alteration of tRNAGly acceptor stem length. (B) Specificity of tRNAGly EXbp11-directed antitermination. (Lanes 1–3) Wild-type glyQS template DNA (GGC specifier sequence, A158 antiterminator); (lanes 4–6) glyQS-UGC template DNA (UGC cysteine specifier sequence); (lanes 7–9) glyQS-A158U template DNA (A158U antiterminator); (lanes 10–12) glyQS-UGC/A158U template DNA (UGC cysteine specifier sequence, A158U antiterminator).