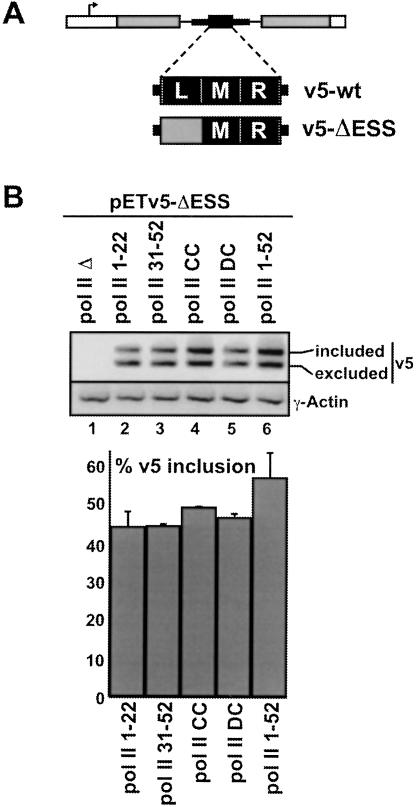
FIGURE 4.
The CTD-length dependence for efficient inclusion of the CD44 v5 exon is influenced by an exonic splicing enhancer sequence. (A) Location of functionally mapped cis-acting sequences (L, M, R) in the CD44 v5 exon (Konig et al. 1998). L and M contain ESS sequences, whereas R contains an ESE element. Substitution of L with sequences from the pBluescript cloning vector in construct pETv5-ΔESS results in increased inclusion of v5 from this reporter (named pETv5–ΔLblue in Konig et al. 1998). (B) 293 cells were transfected with expression plasmids for each of the pol II deletion mutants, then with pETv5–ΔESS, as described in Fig. 2 ▶. RNA was recovered and analyzed by RT-PCR using the primers indicated in Fig. 3A ▶. The bar graph shows quantification of v5 inclusion levels, as measured in Fig. 3 (B, C) ▶, from three independent experiments.