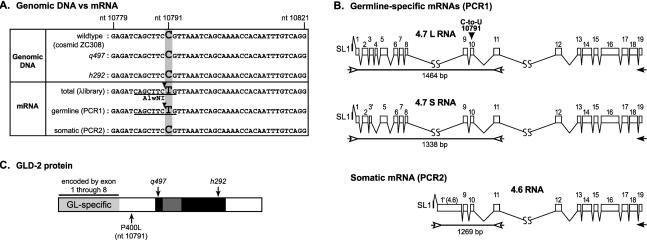
FIGURE 1.
Germline-specific gld-2 transcripts undergo C-to-U editing. (A) Comparison of sequences derived from genomic DNA and cDNA. Genomic DNA: The sequences of genomic DNA were derived from three sources. The sequence of cosmid ZC308 was determined by the C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. ZC308 carries a 19,559-bp insert of wild-type C. elegans genomic DNA, including the region that encodes all the gld-2 transcripts. It possesses a C at position 10791. The other two sequences were derived from PCR products (designed to include the region that contains nucleotide 10791) from genomic DNA of two gld-2 mutants, gld-2(q497) and gld-2(h292). These two mutants have nucleotide-substitution mutations elsewhere in the gld-2 gene, and were confirmed in the sequence analysis (see Wang et al. 2002). However, both DNAs possessed a C at position 10791, corroborating the C at position 10791 in the cosmid sequence. mRNA: Sequences of germline and somatic mRNAs were derived in three ways. The first was derived from the sequence of a gld-2 cDNA clone isolated from a phage cDNA library. The library was prepared using total mRNA extracted from mixed-stage worms (including both germline and somatic tissues). A T was detected at position 10791, indicating editing from C to U in the mRNA. The second analysis (“germline-specific mRNAs [PCR1]”) detected germline-specific transcripts. It was performed using the PCR1 reaction (B), using primers in exons 1 and 11. Two germline-specific transcripts exist, designated 4.7L and 4.7S, differing in the use of an exon 3 splice site and inclusion or exclusion of exon 4. The sequence of these PCR products includes a T at position 10791. The third analysis (“somatic mRNAs [PCR2]”) specifically identifies the 4.6-kb somatic mRNA, which carries a C at position 10791, matching genomic DNA. PCR was performed using a primer in the first exon of the somatic mRNA (exon 1 [4.6]), which is missing in germline-specific mRNAs. Underline, AlwNI site. AlwNI cleaves the CAGNNNCTG sequence, which is found in the region of cDNAs but not genomic DNA. Arrowhead, position of cleavage by AlwNI. (B) gld-2 exon/intron structure: two germline-specific transcripts and one soma-enriched transcript. The two germline-specific transcripts, 4.7L and 4.7S, are detected in the PCR1 reaction. This PCR reaction used primers in exons 1 and 11 (open arrows). Exon 1 is present only in germline-specific mRNAs. Exon 1′ (4.6) is present only in the 4.6-kb RNA that is highly enriched in somatic cells. For PCR1 and PCR2 reactions, the primer indicated by a black arrow (in exon 19) was used to prime the reverse transcriptase on total mRNA from mixed-stage worms and q224 worms (germline-less worms), respectively (see Materials and Methods for details). Open boxes, exons; thin lines, introns; arrows, PCR primers; black arrowhead, position of nucleotide 10791 in exon 10. All the gld-2 mRNAs are trans-spliced to SL1. The lengths of the predicted PCR products derived from mRNAs are indicated below the lines. For additional information on mRNA analysis, see Wang et al. (2002). (C) Schematic diagram of the GLD-2 protein sequence. GL-specific, germline-specific region, encoded by exons specific to the germline transcripts corresponding to the 4.7S and 4.7L RNAs (Wang et al. 2002). Black and dark gray, central and catalytic domains of the GLD-2 nucleotidyltransferase (Aravind and Koonin 1999; Wang et al. 2002); light gray, region of GLD-2 protein present only in the germline.