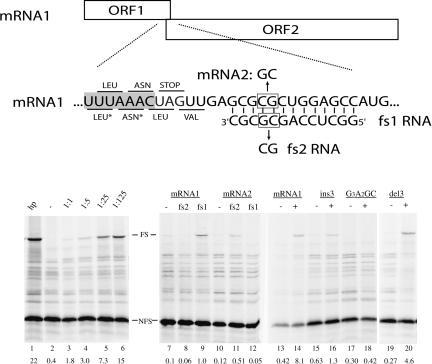
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of the frameshift reporter construct. ORF1 (19 kD) is in the 0-frame, ORF2 (46 kD) is in the −1-frame with respect to ORF1. The −1 frameshifting is monitored by the appearance of the 65-kD fusion product. The UUUAAAC slippery sequence is indicated by shading. The 0-reading frame codons are indicated above the sequence, the −1 frame codons below the sequence. (*) Note that during frameshifting, tRNAs for Leu and Asn simultaneously slip into the −1 frame. In mRNA2, two mutations were introduced to restore base-pairing with fs2 RNA. mRNAs were synthesized by SP6 polymerase from a DNA template. SDS–polyacrylamide gel showing [35S]methionine proteins obtained after in vitro translation using rabbit reticulocyte lysate (Promega) as described previously (ten Dam et al. 1994). (Lane 1) A 12-bp hairpin reference; (lanes 2–6: 0, 0.25, 1.25, 6.25, 31.25) pmol of fs1 RNA (IBA GmbH), respectively, were added to 0.25 pmol of mRNA1 and kept at room temperature for 10 min. Reticulocyte lysate was added and incubation was continued for 1 h at 28°C; (lanes 7–9) mRNA1 without, with 40-fold excess fs2 or fs1 RNA, respectively; (lanes 10–12) mRNA2, without, with 40-fold excess fs2 or fs1 RNA, respectively. Note that overall frameshift values for lanes 7–12 are low due to a 30-min incubation time. (Lanes 13,14) mRNA1 without and with 40-fold excess of fs1, respectively; (lanes 15,16) as in lanes 13 and 14, but with insertion of 3 nt downstream of stopcodon in mRNA1; (lanes 17,18) as in lanes 13 and 14, but with slippery sequence mutant GGGAAGC; (lanes 19,20) as in lanes 13 and 14, but with deletion of 3 nt downstream of stopcodon in mRNA1. Migration of 0-frame and frameshifted product are indicated by NFS and FS, respectively. Band intensities were measured by phosphorimaging (Bio-Rad). Frameshifting percentages were calculated as the fraction of FS product divided by the sum of FS and NFS products after correction for methionine content of both products. Indicated values are the average percentage of at least two independent assays.