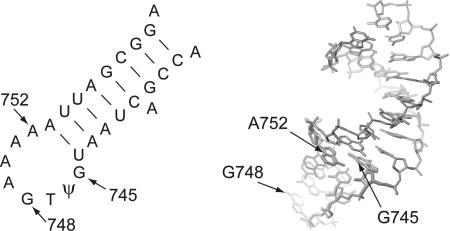
FIGURE 1.
(Left panel) Secondary structure of the E. coli 23S rRNA stem–loop containing the target nucleotides for the RlmAI and RlmAII methyltransferases at G745 and G748, respectively. Base substitutions were made at G745 and A752 by site-directed mutagenesis. The Acinetobacter rRNA has essentially the same sequence. (Right panel) Tertiary fold of same stem–loop determined by NMR (Lebars et al. 2003); the structure is an average of the 17 coordinate sets in the database file. The sheared base pair between G745 and A752 is evident. The N-1 of G745 is oriented toward the RNA major groove; the N-1 of G748 is more readily accessible at the tip of the hairpin loop. The structure of the E. coli RlmAI has recently been solved, and a mechanism of substrate recognition has been proposed (Das et al. 2004).