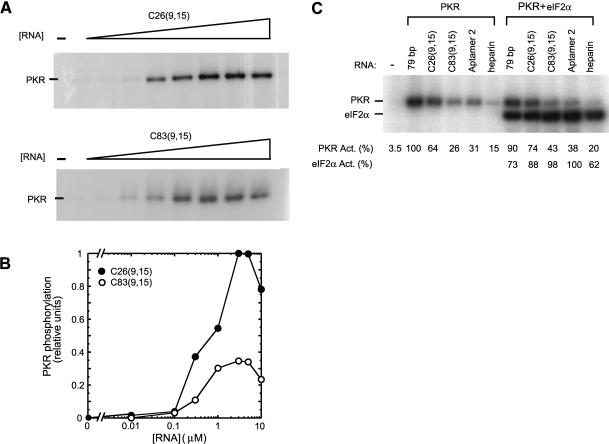
FIGURE 4.
Activation of PKR by aptamers. (A) In vitro activation assay of PKR by selected RNAs. Aptamers C26(9,15) and C83(9,15) were examined for their ability to activate purified PKR kinase. Denaturing 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gels are shown. Concentrations of RNAs were 0, 0.01, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 3.0, 5.0, and 10 μM. The position of phosphorylated PKR is noted. Both clones were found to be potent activators of PKR. (B) Quantitation of the gels in panel A. The two experiments were run under identical electrophoresis and exposure conditions, and so were normalized to the same maximum. Note also that C26 and C83 were loaded on the same gel in panel C to facilitate comparison and give similar behavior confirming the reproducibility of the data. Both clones display a classic bell-shaped activation profile. (C) Comparison of PKR activation by C26 and C83, as well as the reference activators: 79-bp dsRNA, aptamer 2 (from a prior selection) (Bevilacqua et al. 1998), and heparin. PKR was incubated with 0.3 μM of C26, C83, and aptamer 2; 0.1 μM of 79-bp dsRNA; and 0.1 unit/μL heparin. The different RNA concentrations allowed similar band intensities to be observed on the gel. For the right panel, reaction mixtures also included 3 μM eIF-2α. Positions of phosphorylated PKR and eIF2α are noted. Normalized phosphorylation activities for PKR and eIF2α are presented under the gel; note that PKR and eIF2α activities were normalized separately.