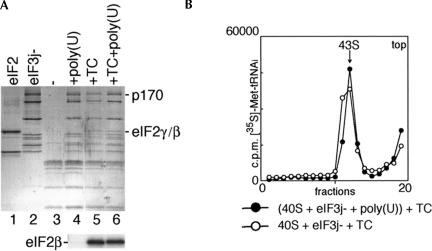
FIGURE 4.
Binding of eIF2-ternary complex (TC) and eIF3j− to 40S subunits in the presence and absence of poly(U) RNA. (A) Detection of eIF2 and eIF3j− in ribosomal complexes isolated from sucrose density gradients. eIF2 (lane 1), eIF3j− (lane 2), 40S subunits (lane 3), 40S/eIF3j− binary complexes formed in the presence of poly(U) (lane 4), 43S ribosomal complexes formed from purified TC and preassembled eIF3j−/poly(U)/40S subunit complexes (lane 6), and 43S complexes assembled using TC, eIF3j− and 40S subunits (lane 5) were analyzed by gel electrophoresis followed by Coomassie staining (lanes 1–6 of the upper panel) or Western blotting with eIF2βantibodies (lanes 4–6 of the lower panel). eIF3a (p170 subunit) and eIF2β,γ are labeled to the right of the upper panel; eIF2β is labeled to the left of the lower panel. (B) Incorporation of aminoacylated [35S]Met-tRNAiMet into 43S complexes, assembled either from TC and preassembled eIF3j−/poly(U)/40S subunit complexes or from 40S subunits, eIF3j−, and TC. Ribosomal complexes were separated by centrifugation in 10%–30% linear sucrose gradients. Sedimentation was from right to left. The position of 43S complexes is indicated. Upper fractions from the gradient have been omitted for clarity.