FIGURE 2.
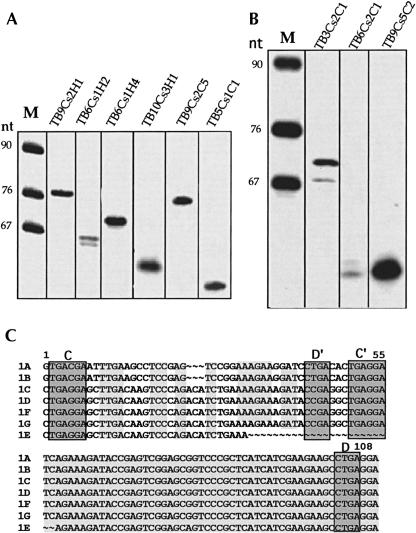
Expression studies on the predicted snoRNAs. (A) Primer extension analysis of snoRNAs present in different clusters. Total RNA was subjected to primer extension with the following primers (50,000 cpm in each reaction): Tbsno-H1, 2-CH-2, 2-HH-3, and TB5H1 specific for the H/ACA-like snoRNAs TB9Cs2H1, TB6Cs1H2, TB6Cs2H4, and TB10Cs3H1, respectively. Primers TbsnoC4 and Tb5C1 were used to detect C/D snoRNAs TB9Cs2C5 and TB5Cs1C1, respectively. The identity of each snoRNA is indicated above the lane. (Lane M) A pBR322 MspI digest was used as a marker. (B) Expression studies on snoRNAs present in clusters with unique properties. Primer extension analyses were performed using primers TBcr03, TB6C2-A, and TB9Cs5-A, specific to TB3Cs2C1, TB6Cs2C1, and TB9Cs5C2, respectively. The extension product was analyzed on 6% polyacrylamide–7 M urea gel. (Lane M) Labeled marker of a pBR322 MspI digest. The sizes are indicated in nucleotides. (C) Sequence alignment of different copies of TB3Cs2C1. The potential C/D and C′/D′ domains are boxed. The conserved sequences are shown in shadow. 1A–1G reflect the different copies of the same snoRNA present in the cluster. The missing nucleotides are shown as “~.” Sequence alignment was performed using the program Pileup from the GCG package.