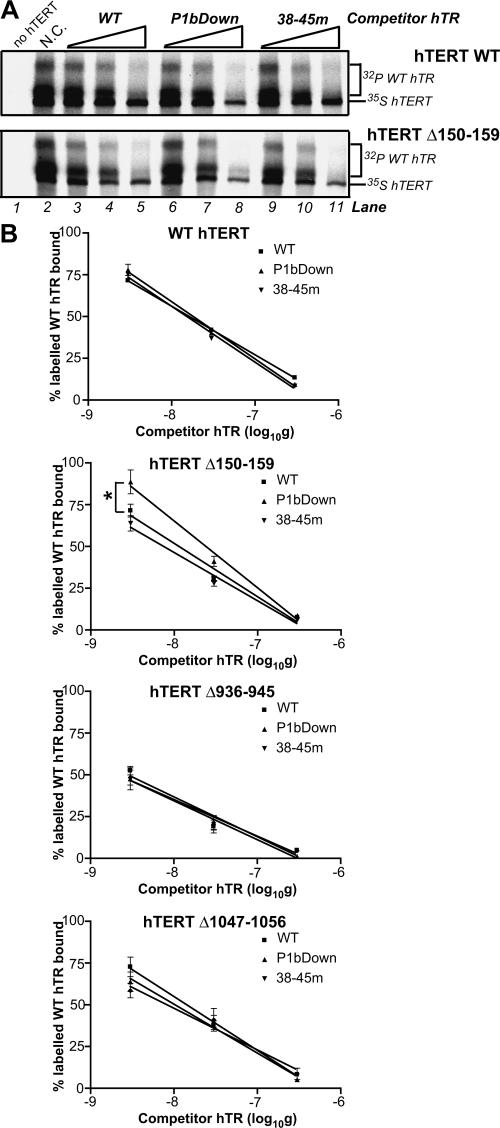
FIGURE 4.
hTERT-hTR interactions in mutant telomerases with altered 5′ template usage phenotypes. (A) Representative immunoprecipitation- based competitive hTR–hTERT interaction assays performed with wild-type (WT) hTERT and the Δ150–159 hTERT mutant. The positions of hTR and hTERT are indicated at the right of each panel. Increasing concentrations of the indicated unlabeled hTRs (lanes 3–11) were added to RRL reconstitution mixtures containing identical amounts of 32P-labeled wild-type hTR. This approach ensured that each sample contained exactly the same amount of labeled input hTR and eliminated the large experimental variation that we frequently observed when different hTR variants were individually labeled and immunoprecipitated in the absence of competitors (data not shown). ′ Immunoprecipitations were performed with an antibody against hTERT. Control reactions performed in the absence of competitor (N.C.) and hTERT are shown in lanes 1 and 2. (B) Quantification of the percent labeled wild-type hTR bound after reconstitution and immunoprecipitation in the presence of increasing concentrations of unlabeled competitors (identified in keys). The wild-type hTR signal intensities for competition samples were expressed as a percentage of the wild-type hTR signal in control reactions performed in the absence of competitor (100%).