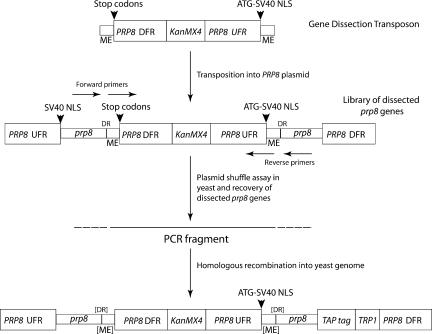
FIGURE 1.
Structure of the gene dissection transposon and dissected prp8. The transposon was custom-built from three main components: (1) PRP8 gene downstream flanking region (DFR) containing signals for transcription termination, polyadenylation, and stop codons in all three reading frames; (2) KanMX4 cassette (Wach et al. 1994) conferring Kanamycin-resistance in Escherichia coli and G418-resistance in yeast (KanMX4); (3) PRP8 gene upstream flanking region (UFR) containing signals for initiation of transcription and translation. The transposon is flanked by 19 bp “Mosaic End” (ME) sequences recognized by Tn5 transposase. An example of the structure of one of a library of transposon-dissected prp8 genes is shown (not to scale). The transposon terminates transcription and translation of the upstream prp8 gene sequences and drives expression of the prp8 gene sequences downstream, producing two contiguous protein fragments via translation of two separate mRNAs. Each fragment is tagged at its N terminus with a nuclear localization signal (NLS). The disrupted alleles were introduced into the TAP-tagged chromosomal copy of PRP8 in yeast strain RG8T by homologous recombination using PCR-amplified DNA; the outer primer set was for partition after codon 436, and the inner primer set was for partition after codons 770 and 2173 to avoid generating the 9-bp direct repeat (DR) generated during transposition.