Figure 2.
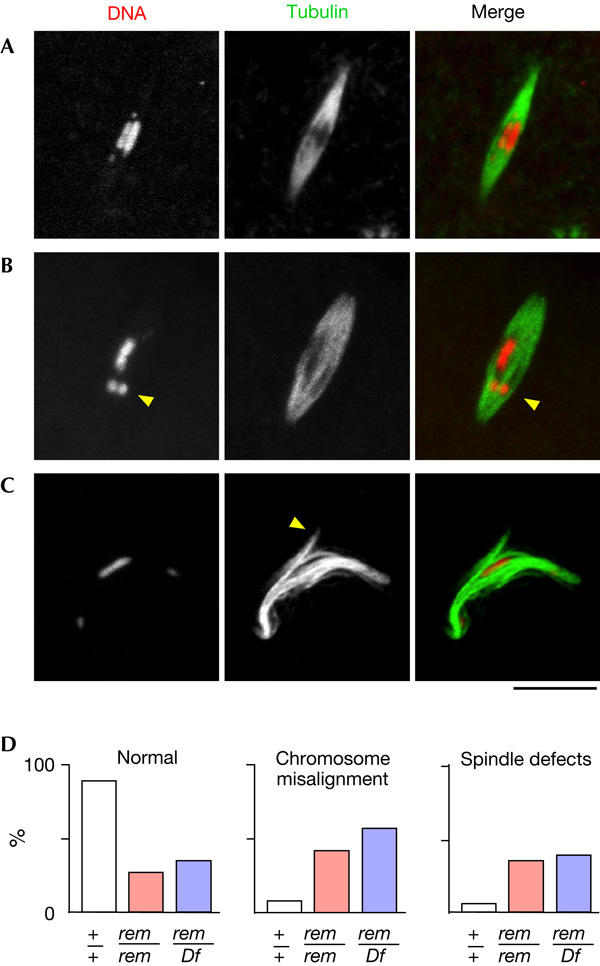
Cks30A is essential for spindle morphogenesis and chromosome alignment. The spindle and chromosomes in non-activated oocytes were visualized by immunostaining in wild type (A) and in the rem1 mutant (B,C). Spindle abnormality and chromosome misalignment in the rem1 mutant. The arrowheads in (B,C) indicate a mispositioned/misorientated chromosome and an ectopic spindle pole formed near the equator, respectively. Spindles are longer in the rem+ mutant (21.1±5.7 μm) than in wild type (14.7±5.8 μm). (D) Quantification of the spindle and chromosome defects in wild type (+/+), rem1 homozygotes (rem/rem) and hemizygotes (rem/Df). Between 29 and 135 spindles were counted for each genotype. The differences between wild type and rem1 homozygotes (or hemizygotes) are significant (P<0.001), whereas the differences between rem homozygotes and hemizygotes are not (P=0.84). Scale bar, 10 μm.
