Figure 4.
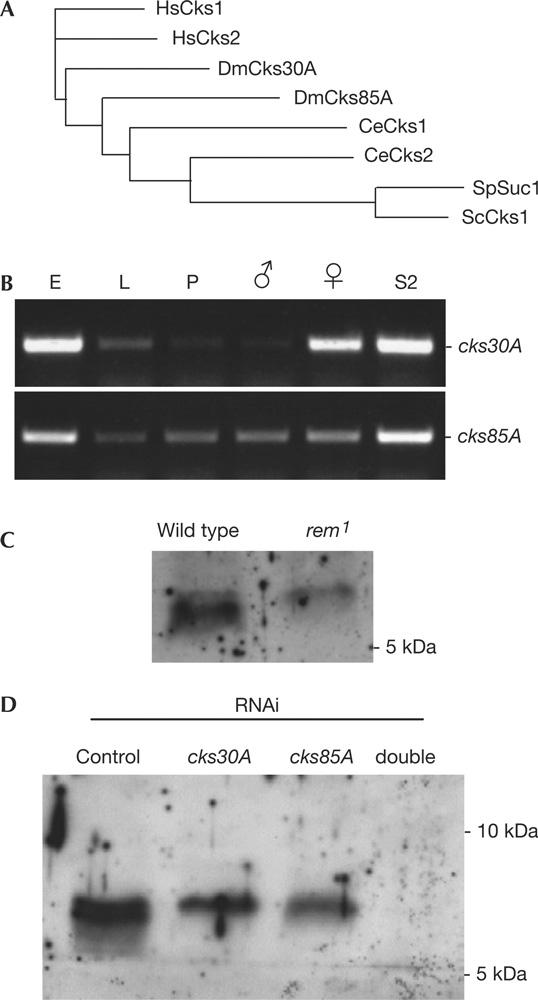
Two Cks homologues in Drosophila. (A) Phylogram of the Cks homologues in various organisms. The cores of 66 amino acids were compared by ClustalW at EBI. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans, Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Hs, Homo sapiens; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe. (B) Expression of the two cks genes during Drosophila development. RNA was isolated from embryos (E), third-instar larvae (L), early pupae (P), adult males, adult females and S2 cells (from left to right). Transcripts of cks30A and cks85A were detected from 0.2 μg of RNA by reverse transcription–PCR with 30 cycles. (C) Cks proteins in embryos laid by wild type and rem1. Embryos (0–12 h) were used for immunoblots that were probed with an antibody against human Cks1. The lower band is greatly reduced in the rem1 mutant. (D) Identification of Cks proteins in S2 cells. S2 cells were treated with doublestranded RNA corresponding to cks30A and cks85A for 7 days before analysis by immunoblots using an antibody against human Cks1. From the left: control RNA interference (RNAi; bacterial β-lactamase), cks30A single RNAi, cks85A single RNAi and cks30A cks85A double RNAi.
