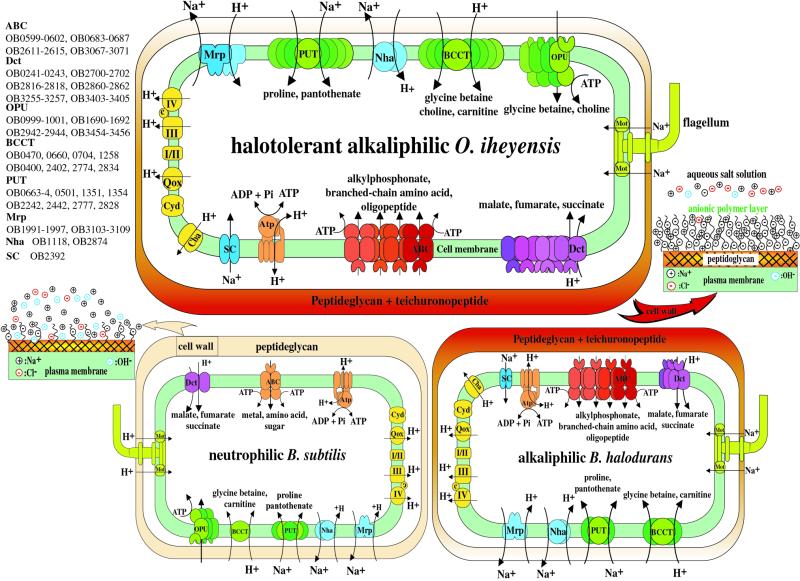
Figure 5.
Overview of putative major transport systems that govern alkaliphily and extreme halotolerance in O.iheyensis. Overview of the cell wall system and the enzymes involved in the respiratory chain (yellow) are also shown. Transporters are grouped by their category: sodium cycle (blue), organic osmotic solutes such as glycine betaine, choline, carnitine, proline and pantothenate (green), carboxylic acids such as malate, fumarate and succinate (purple) and peptides and amino acids (red). ABC transport systems are shown as composite figures of oval, circular and sickle shape. The gene number of O.iheyensis corresponding to each component of the transporter is described below or above each figure. Atp, F1F0 ATP synthase; ABC, ABC transporter; BCCT, glycine betaine, carnitine/H+ symporter; Cba, cytochrome c oxidase (bo3-type); Cyd, cytochrome bd oxidase; I, NADH dehydrogenase; II, succinate dehydrogenase; III, menaquinol cytochrome c oxidoreductase; IV, cytochrome caa3 oxidase; Dct, C4-dicarboxylate transport system; Mrp, Na+/H+ antiporter; Mot, channel for energization of motility; Nha, Na+/H+ antiporter; OPU, glycine betaine ABC transporter; PUT, proline/Na+ symporter and pantothenate/Na+ symporter; and Qox, cytochrome aa3 quinol oxidase; Sc, voltage-gated sodium channel.