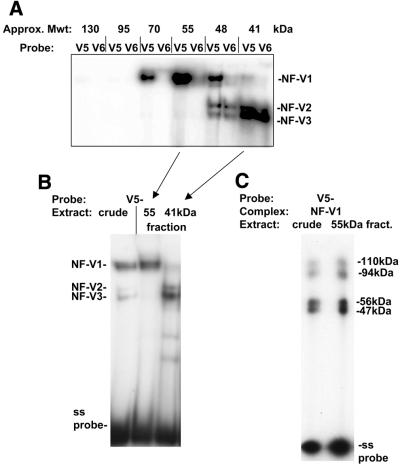
Figure 6.
Nuclear dbpA may bind to the VEGF HR region as a dimer. (A) Balb/c 3T3 crude nuclear extract was fractionated by FPLC gel filtration and protein in fractions assayed for binding to the VEGF HR region single strand oligonucleotide (V5–) or to the CSD protein-binding site mutant (V6–) in a gel retardation assay. Consecutive 0.5 ml fractions containing NF-V1-binding activity are shown. NF-V1 to NF-V3 complexes are indicated. The approximate sizes of protein fractions, determined by comparison to elution profiles of protein standards, is given in kDa. (B) Balb/c 3T3 crude nuclear extract and gel filtration fractions containing the peak of NF-V1 activity (55 kDa) and NF-V2/3 activity (41 kDa) are shown bound to the VEGF HR region single strand oligonucleotide (V5–) in a gel retardation assay. Nuclear complexes (NF-V1, NF-V2 and NF-V3) and free single strand probe (ss probe) are indicated. (C) NF-V1 complexes from crude nuclear and fractionated extract were UV crosslinked to the VEGF HR region oligonucleotide (V5–) and crosslinked proteins analyzed by SDS–PAGE. The sizes of crosslinked proteins are indicated and were calculated by subtraction of the molecular weight of the V5– probe.