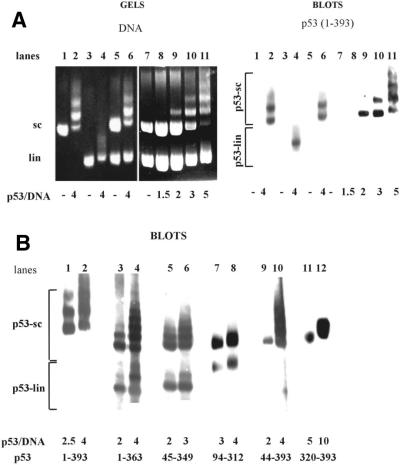
Figure 2.
p53 deletion mutants bind scDNA with different selectivities in competition experiments. (A) scDNA (0.3 µg; lanes 1 and 2) or linDNA (0.3 µg; lanes 3 and 4) alone was incubated with p53b(1–393) protein (lanes 2 and 4) at a p53 tetramer/DNA molar ratio of 4. A mixture of linear and supercoiled (sc/lin ratio 1:1) forms of pBluescript DNAs containing in total 0.6 µg (lanes 5 and 6), 0.8 µg (lanes 7, 10, 11) or 1.6 µg (lanes 8 and 9) was incubated with p53b(1–393) protein in the molar ratio range 1.5–5.0 protein (tetramer)/DNA (lanes 6 and 8–11). Samples were run on 1.3% agarose gels in 0.33× TBE and stained with ethidium bromide (left). Note that under the conditions used linDNA migrates faster than scDNA. The gels were blotted (right) and p53–scDNA (p53-sc) and/or p53–linDNA (p53-lin) complexes were detected using DO-1 antibody. (B) Immunoblots of two representative lanes showing results of the competition assays with the following proteins: lanes 1 and 2, p53(1–393); lanes 3 and 4, p53(1–363); lanes 5 and 6, p53(45–349); lanes 7 and 8, p53(94–312); lanes 9 and 10, p53(44–393); lanes 11 and 12, p53(320–393). Mouse monoclonal antibodies DO-1 (recognizing amino acids 20–25), DO-11 (amino acids 176–185), DO-12 (amino acids 256–270), Bp53-6.1 (amino acids 381–390), Bp53-10.1 (amino acids 375–379) and ICA-9 (amino acids 388–393) were applied to detect epitopes present within the p53 proteins.