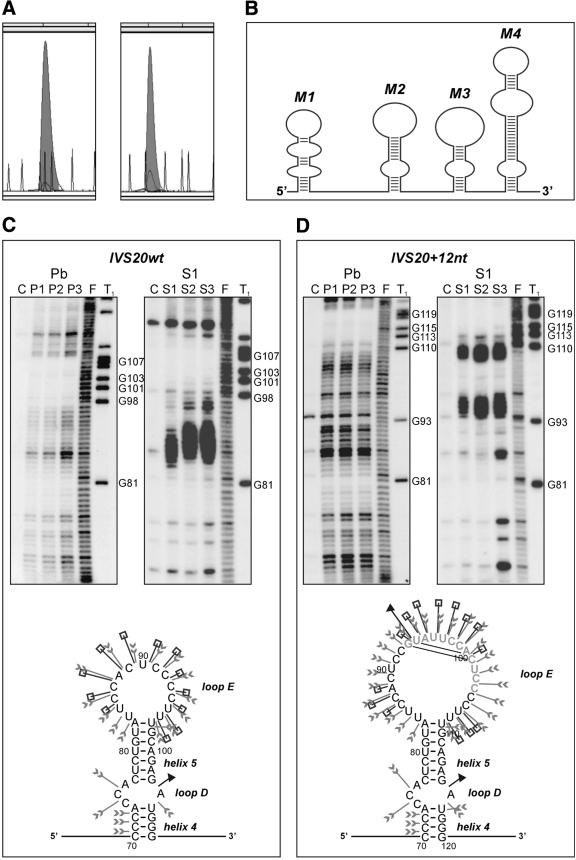
Figure 2.
Structure analysis of two BRCA1 intron 20 transcripts: wild-type IVS20wt and containing a 12 nt duplicated sequence IVS20+12nt. (A) CE in non-denaturing conditions of IVS20wt (left) and IVS20+12nt (right) transcripts fluorescently labeled at their 3′ end with TdT and [R110]dUTP (shadowed peaks); ROX-1000 internal standard (gray line). (B) Schematic illustration of the experimentally determined IVS20wt transcript secondary structure. Four independent structure modules (M1–M4) are shown. (C) (Top) Denaturing 6% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 5′-end radiolabeled RNA fragments generated from IVS20wt (left) and IVS20+12nt (right), treated with lead ions (lane Pb) at a concentration of: P1, 0.25 mM; P2, 0.5 mM; P3, 1 mM; and S1 nuclease (lane S1) at a concentration of: S1, 0.5 U/µl; S2, 1 U/µl; S3, 2 U/µl (1 mM ZnCl2 was present in each reaction); lane C, incubation control (no probe); lane F, formamide ladder; lane T1, guanine-specific ladder. Selected guanine residues are numbered according to their positions in the sequence. (Bottom) Proposed secondary structure of the module M2 distinguishing the IVS20wt and IVS20+12nt transcripts. Cleavage sites and intensities are specified for each of the three probes used in this analysis (arrowheads, lead ions; squares, S1 nuclease; and triangles, T1 ribonuclease). RNA structure motifs are also indicated. The other three RNA structure modules are the same in both transcripts. (D) (Top) As in (C, top), but for IVS20+12nt transcript; (bottom) as in (C, bottom), but for M2+12nt module; the inserted 12 nt are shown in gray.