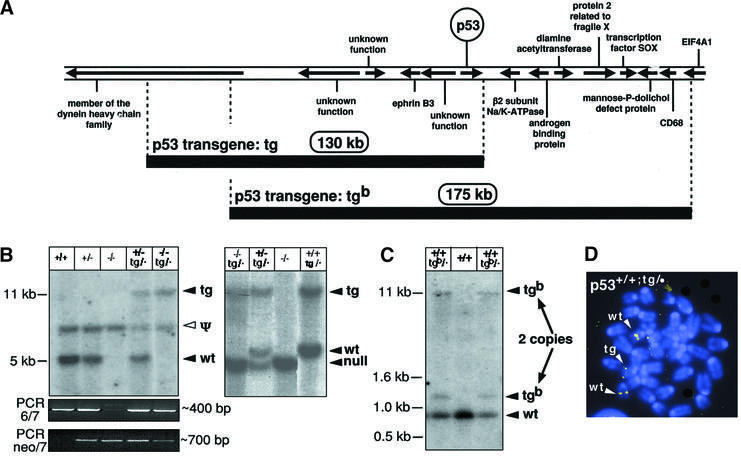
Fig. 1. Strategy to increase the gene dosage of p53. (A) Map of the genomic segments used to generate the ‘super p53’ mice. The map is based on the ENSEMBL Mouse Genome Database and shows the approximate position of the transcriptional units surrounding the p53 gene. The exact position of the limits of the two BACs used in this work was determined from their terminal sequences. The sizes of the two genomic inserts were determined experimentally by pulsed-field electrophoresis, and both are compatible with the predicted sizes from the ENSEMBL Mouse Genome Database. (B) Identification of the p53-tg allele by Southern blotting. ScaI-digested genomic DNA from mice of the indicated genotypes was hybridized with a probe that detects either exon 6 of p53 (absent in the p53 null allele; see Jacks et al., 1994; and Supplementary data) (left panel) or a region immediately downstream of exon 11 (after the p53 transcriptional unit; see Supplementary data) (right panel). These strategies allow the detection of fragments containing the junction between BAC-p53-tg and the surrounding DNA at the insertion site (see Supplementary data). Genotyping was confirmed further in combination with PCR data, according to the strategy described in Jacks et al. (1994) to amplify the region between exons 6 and 7 (present in the wild-type and tg alleles) and the region between the neo marker and exon 7 (present in the null allele) (bottom panels). The existence of a p53 pseudogene detected with exonic probes is well established (see for example Jacks et al., 1994), and the band resulting from it (marked as Ψ) is common to all DNA preparations independently of p53 genotype. Mice carrying the p53-tg allele exhibit a single additional band in both types of Southern blots (marked as tg), indicative of a single BAC-p53-tg copy. (C) Identification of the p53-tgb allele by Southern blotting. EcoRI-digested genomic DNA from mice of the indicated genotypes was hybridized with a probe that detects a terminal fragment of BAC-p53-tgb. This strategy allows the detection of fragments containing the junction between BAC-p53-tgb and the surrounding DNA at the insertion site (see Supplementary data). Mice carrying the p53-tgb allele exhibit two additional bands (marked as tgb), indicative of two BAC-p53-tgb copies. These two copies co-segregated along mouse generations, indicating that they are genetically linked. (D) Identification of the p53-tg allele by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Representative example of a metaphase derived from p53+/+;tg/· MEFs and hybridized with the entire BAC-p53-tg. The endogenous alleles are known to be located at a central region in chromosome pair 11. Control metaphases from wild-type mice gave only two pairs of signals at a central position (data not shown). In the p53+/+;tg/· metaphases, a third pair of signals appears located in the telomeric region of a non-identified chromosome.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.