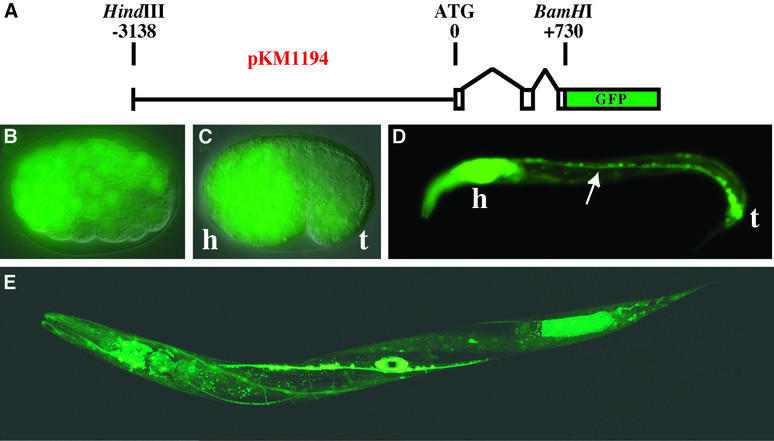
Fig. 2. Embryonic and larval expression of adr-1 in C.elegans. (A) The diagram shows the pKM1194 reporter construct used to generate adr-1::GFP expression lines (KM163–5). Nomarski/GFP merged images show that adr-1::GFP is expressed by late gastrulation (B, ≥100 cell stage), and by the comma stage (C) is predominantly neuronal (h, presumptive head; t, tail). Neuronal expression continues into larval stages as shown for an L1 worm (D), where expression was observed in the ventral nerve cord (arrow), along with intense expression in the head ganglia and nerve ring (h) and the tail neurons (t). A confocal image of a late L4 worm (E) shows expression in most cells of the nervous system, as well as in the developing vulva (see also Figure 3). Other tissues with weak expression include the pharynx and body wall muscle. We were unable to determine whether the expression in posterior intestinal cells is true adr-1 expression or an artifact of transgenic expression (Mello and Fire, 1995).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.