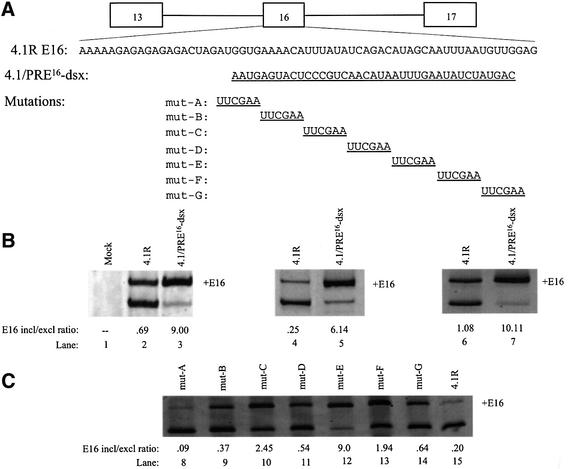
Fig. 2. Mutation of CE16 activates E16 inclusion. (A) 4.1R minigene and E16 wild-type sequence with 4.1/PRE16-dsx, and linker-scan sequence substitutions (underlined) in E16 aligned below. All mutant constructs are the same length as the wild-type minigene. (B) RT–PCR assay of spliced products from wild-type 4.1R minigene and the PRE16-dsx substitution mutation. In vivo splicing in transfected HeLa cells (lanes 1–3), in HeLa nuclear extract (lanes 4 and 5) and in Xenopus oocytes (lanes 6 and 7) with the E16 inclusion/exclusion ratio. (C) RT–PCR results of in vitro splicing of CE16 linker-scanning mutations of the 4.1R minigene in HeLa nuclear extract (lanes 8–15).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.