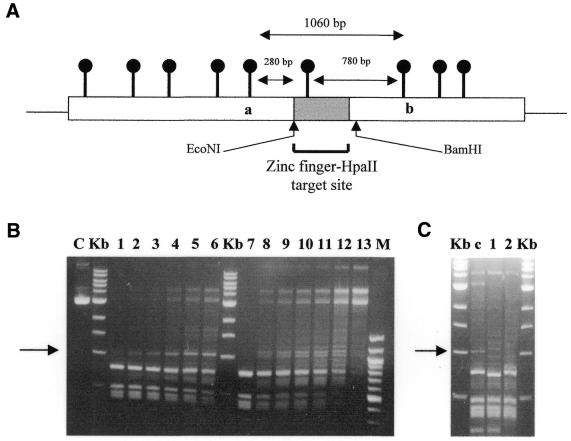
Figure 7.
Ex vivo methylation analysis of Zf.M.HpaII interacting with target site-containing plasmid DNA. (A) Schematic outline of the key elements of the ZMTopo vector used as substrate in the ex vivo studies described below (see also Materials and Methods). The region of the plasmid harbouring the zinc finger and single flanking HpaII site is shown as a grey box with a lollipop on it. In the scenario where this site has been preferentially methylated (designated by a black lollipop, compared to unmethylated vector HpaII sites, shown in grey), the nearest cleavage by R.HpaII will only occur at flanking HpaII sites a and b, resulting in the generation of a 1060 bp fragment. If this site is not methylated, derivative fragments of ∼280 and 780 bp will be produced. Restriction enzyme sites for EcoNI and BamHI are also shown. These sites are unique to DNA fragments harbouring the target sequence. (B) Target site-containing vector ZMTopo was incubated with increasing amounts of Zf.M.HpaII or M.HpaII enzyme for 30 min prior to digestion with R.HpaII. Lanes 1–6 and 7–12 represent digestion of vector preincubated with 25, 50, 75, 125, 175 and 225 fmol Zf.M.HpaII and M.HpaII protein, respectively. The expected 1060 bp DNA fragment indicative of targeted methylation is arrowed. Lane U, unrestricted ZMTopo DNA; lane C, unmethylated vector DNA restricted with R.HpaII; lane M, 100 bp ladder (NEB). Key size bands are indicated. (C) All lanes were identical to those described for lane 4 in (B), but with the inclusion of 10 U of the restriction enzyme EcoNI (lane 1) or BamHI (lane 2) or just water (lane c). The 1060 bp DNA fragment present in lane c is arrowed.