Abstract
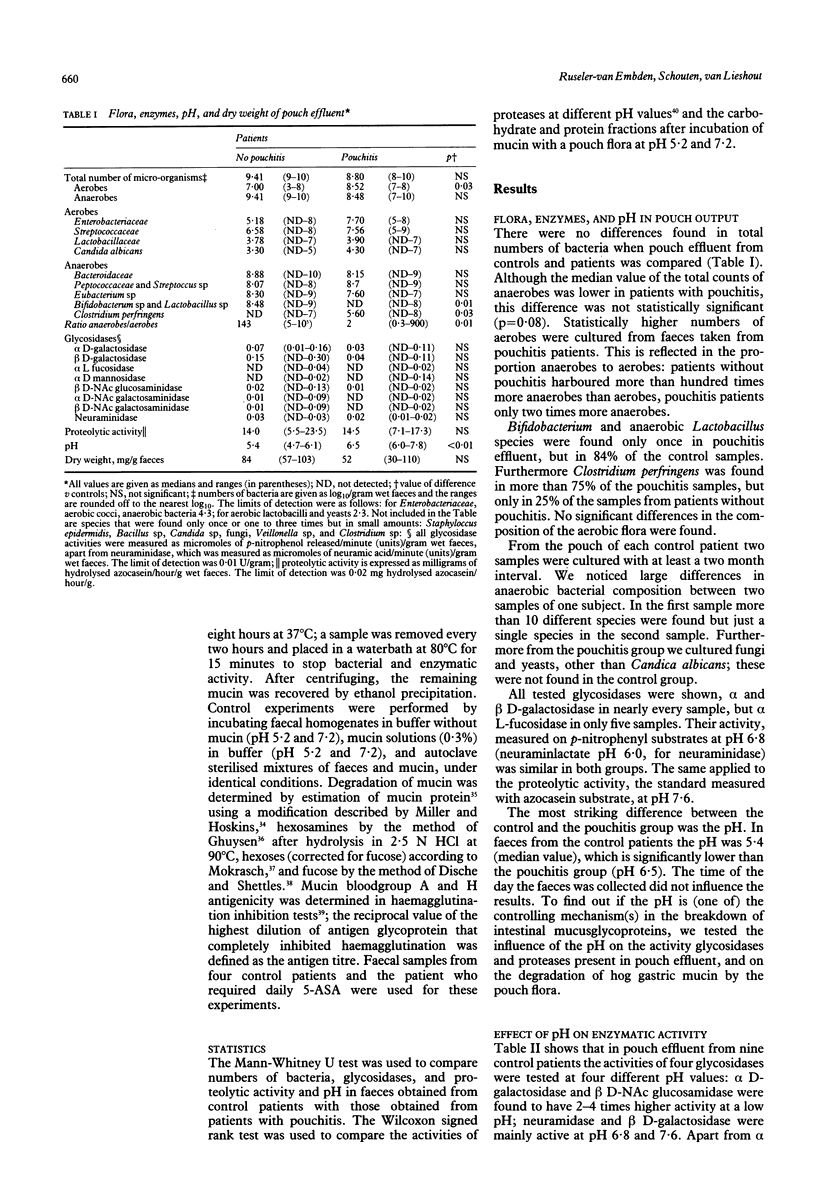
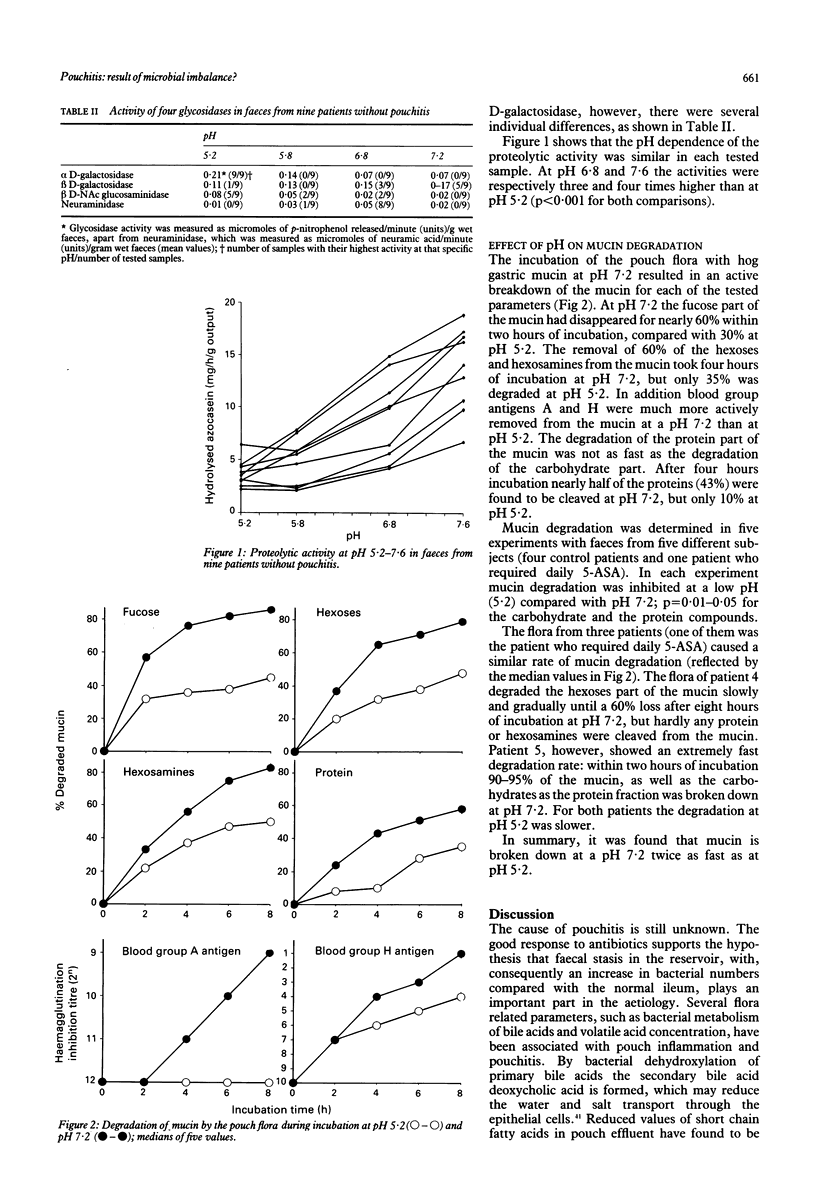
To elucidate the role of microbiological factors in pouchitis, this study investigated the composition of ileal reservoir microflora, the mucus degrading capacity of bacterial enzymes as well as the pH and the proteolytic activity of pouch effluent. Stool samples were collected from five patients with pouchitis and nine patients without pouchitis. The flora of patients with pouchitis had an increased number of aerobes, a decreased ratio anaerobes to aerobes, less bifidobacteria and anaerobic lactobacilli, more Clostridium perfringens, and several species that were not found in control patients (for example, fungi). Furthermore the pH was significantly higher in patients with pouchitis (median value 6.5) than in control patients (5.4). To find out if the pH might influence the breakdown of intestinal mucus glycoproteins, the activity of glycosidases and proteases, and the degradation of hog gastric mucin by the pouch flora was tested at pH 5.2-7.6. Some glycosidases were inhibited, others were stimulated by a low pH, however, in each sample the proteolytic activity was inhibited for 75% at pH 5.2 compared with pH 6.8 and 7.6. Degradation of hog gastric mucin by the pouch flora was an active process at pH 7.2: within two to four hours of incubation more than half of the mucin was degraded. At pH 5.2 it took twice as long. It is concluded that pouchitis possibly results from instability of the flora in the pouch, which causes homeostasis to disappear (dysbiosis), and the protection of the pouch epithelium by the mucus layer becomes affected by increased activity of bacterial and host derived enzymes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A., Leonard A. Mucus structure. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1985;9(12 Pt 2):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambroze W. L., Jr, Dozois R. R., Pemberton J. H., Beart R. W., Jr, Ilstrup D. M. Familial adenomatous polyposis: results following ileal pouch-anal anastomosis and ileorectostomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 Jan;35(1):12–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02053332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss C. E., Houston A. P. Characterization of plant polysaccharide- and mucin-fermenting anaerobic bacteria from human feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):626–632. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.626-632.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borriello S. P., Larson H. E., Welch A. R., Barclay F., Stringer M. F., Bartholomew B. A. Enterotoxigenic Clostridium perfringens: a possible cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Lancet. 1984 Feb 11;1(8372):305–307. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bounous G., Menard D., De Medicis E. Role of pancreatic proteases in the pathogenesis of ischemic enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brevinge H., Berglund B., Kock N. G. Ileostomy output of gas and feces before and after conversion from conventional to reservoir ileostomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 Jul;35(7):662–669. doi: 10.1007/BF02053757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen M. R., Tvede M., Mortensen P. B. Short-chain fatty acids in pouch contents from patients with and without pouchitis after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Gastroenterology. 1992 Oct;103(4):1144–1153. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91497-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield A. P., Warren B. F., Bartolo D. C., Wagner S. A., Clamp J. R. Mucin changes in ileoanal pouches monitored by metabolic labelling and histochemistry. Br J Surg. 1992 Nov;79(11):1209–1212. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800791139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi P., Wideman P. A., Sutter V. L., Drenick E. J., Passaro E., Jr, Finegold S. M. Bacterial flora of the small bowel before and after bypass procedure for morbid obesity. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jan;137(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Macfarlane G. T. The control and consequences of bacterial fermentation in the human colon. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;70(6):443–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb02739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton M. T., Faught W. E., Becker J. M., Burt R. Superior results of ileoanal pull through (IAPT) in polyposis coli vs ulcerative colitis patients. J Surg Res. 1992 Feb;52(2):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(92)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Sutter V. L., Boyle J. D., Shimada K. The normal flora of ileostomy and transverse colostomy effluents. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):376–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemlo B. T., Wong W. D., Rothenberger D. A., Goldberg S. M. Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Patterns of failure. Arch Surg. 1992 Jul;127(7):784–787. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420070036009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Levitan R., Patterson J. F. Studies of intestinal microflora. IV. The microflora of ileostomy effluent: a unique microbial ecology. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):874–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C., Agustines M., McKee W. B., Boulding E. T., Kriaris M., Niedermeyer G. Mucin degradation in human colon ecosystems. Isolation and properties of fecal strains that degrade ABH blood group antigens and oligosaccharides from mucin glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):944–953. doi: 10.1172/JCI111795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högström H., Haglund U., Zederfeldt B. Beneficial effect of proteinase inhibitors on early breaking strength of intestinal anastomoses. Acta Chir Scand. 1985;151(6):529–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. G., Phillips S. F., Kelly K. A., Weinstein W. M., Gilchrist M. J. Dysfunction of the continent ileostomy: clinical features and bacteriology. Gut. 1983 Mar;24(3):193–201. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.3.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laboisse C. L. Structure of gastrointestinal mucins: searching for the Rosetta stone. Biochimie. 1986 May;68(5):611–617. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Borriello S. P. Infectious diarrhea due to Clostridium perfringens. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):390–391. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin K. E., Pemberton J. H., Phillips S. F., Zinsmeister A. R., Pezim M. E. Role of oxygen free radicals in the etiology of pouchitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 May;35(5):452–456. doi: 10.1007/BF02049401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmuller J. L., Pemberton J. H., Dozois R. R., Ilstrup D., van Heerden J. Pouchitis and extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Ann Surg. 1990 May;211(5):622–629. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luukkonen P., Valtonen V., Sivonen A., Sipponen P., Järvinen H. Fecal bacteriology and reservoir ileitis in patients operated on for ulcerative colitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988 Nov;31(11):864–867. doi: 10.1007/BF02554850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOKRASCH L. C. Analysis of hexose phosphates and sugar mixtures with the anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane G. T., Gibson G. R., Cummings J. H. Comparison of fermentation reactions in different regions of the human colon. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;72(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb04882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden M. V., Farthing M. J., Nicholls R. J. Inflammation in ileal reservoirs: 'pouchitis'. Gut. 1990 Mar;31(3):247–249. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen S. G., Hoitsma H., Boot H., Seldenrijk C. A. Pouchitis (pouch ileitis). Neth J Med. 1989 Jun;35 (Suppl 1):S54–S66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. S., Hoskins L. C. Mucin degradation in human colon ecosystems. Fecal population densities of mucin-degrading bacteria estimated by a "most probable number" method. Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen N. Restorative proctocolectomy--the pouch operation: good or bad? Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1992;192:130–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth D. G., Godwin P. G., Dixon M. F., Williams N. S., Johnston D. Ileal ecology after pouch-anal anastomosis or ileostomy. A study of mucosal morphology, fecal bacteriology, fecal volatile fatty acids, and their interrelationship. Gastroenterology. 1989 Mar;96(3):817–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth D. G., Johnston D., Williams N. S., King R. F., Burkinshaw L., Brooks K. Changes in the absorption of bile acids after total colectomy in patients with an ileostomy or pouch-anal anastomosis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1989 Mar;32(3):230–234. doi: 10.1007/BF02554535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. R., Rankin D. R., Weiland L. H., Kelly K. A. Enteric bacteriology, absorption, morphology and emptying after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Br J Surg. 1986 Nov;73(11):909–914. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800731121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Dvorak A. M., Cisneros R. L., McLeod R. S., Antionoli D., Silen W., Blair J. E., Monahan-Earley R. A., Cullen J., Cohen Z. Microbiologic assessment of tissue biopsy samples from ileal pouch patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):312–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.312-317.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena J. P., Gemlo B. T., Rothenberger D. A. Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis: state of the art. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1992 Mar;6(1):113–128. doi: 10.1016/0950-3528(92)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K., Isselbacher K. J. Glycoprotein composition of colonic mucosa. Specific alterations in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Nov;87(5):991–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh S. M., Schoetz D. J., Jr, Roberts P. L., Murray J. J., Coller J. A., Veidenheimer M. C. Pouchitis--is it a wastebasket diagnosis? Dis Colon Rectum. 1991 Aug;34(8):685–689. doi: 10.1007/BF02050351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Bruce A. W., McGroarty J. A., Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Is there a role for lactobacilli in prevention of urogenital and intestinal infections? Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Oct;3(4):335–344. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.4.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roediger W. E. Role of anaerobic bacteria in the metabolic welfare of the colonic mucosa in man. Gut. 1980 Sep;21(9):793–798. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.9.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruseler-van Embden J. G., Both-Patoir H. C. Anaerobic gram-negative faecal flora in patients with Crohn's disease and healthy subjects. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Jun;49(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00393670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruseler-van Embden J. G., Schouten W. R., van Lieshout L. M., Auwerda H. J. Changes in bacterial composition and enzymatic activity in ileostomy and ileal reservoir during intermittent occlusion: a study using dogs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):111–118. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.111-118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruseler-van Embden J. G., van Lieshout L. M. Increased faecal glycosidases in patients with Crohn's disease. Digestion. 1987;37(1):43–50. doi: 10.1159/000199486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruseler-van Embden J. G., van Lieshout L. M. Increased proteolysis and leucine aminopeptidase activity in faeces of patients with Crohn's disease. Digestion. 1988;40(1):33–40. doi: 10.1159/000199640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruseler-van Embden J. G., van der Helm R., van Lieshout L. M. Degradation of intestinal glycoproteins by Bacteroides vulgatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Mar;49(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santavirta J., Mattila J., Kokki M., Matikainen M. Mucosal morphology and faecal bacteriology after ileoanal anastomosis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1991 Feb;6(1):38–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00703959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steadman C. J., Phillips S. F., Camilleri M., Talley N. J., Haddad A., Hanson R. Control of muscle tone in the human colon. Gut. 1992 Apr;33(4):541–546. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.4.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensinck F., Custers-van Lieshout, Poppelaars-Kustermans P. A., Schröder A. M. The faecal flora of patients with Crohn's disease. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Aug;87(1):1–12. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensinck F., Ruseler-van Embden J. G. The intestinal flora of colonization-resistant mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Sep;69(3):413–421. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexner S. D., Jensen L., Rothenberger D. A., Wong W. D., Goldberg S. M. Long-term functional analysis of the ileoanal reservoir. Dis Colon Rectum. 1989 Apr;32(4):275–281. doi: 10.1007/BF02553479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuccaro G., Jr, Fazio V. W., Church J. M., Lavery I. C., Ruderman W. B., Farmer R. G. Pouch ileitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Oct;34(10):1505–1510. doi: 10.1007/BF01537101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. J., de Angelis C. P., Soper N., Kettlewell M. G., Mortensen N. J., Jewell D. P. Clinical and functional outcome after restorative proctocolectomy. Br J Surg. 1991 Sep;78(9):1039–1044. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


