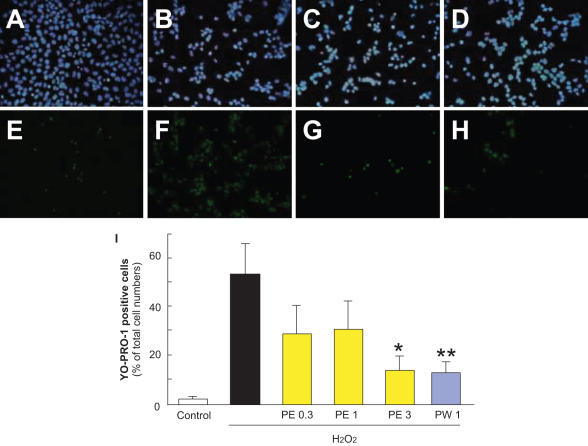
Figure 1.
Representative fluorescence microscopy of Hoechst 33342 (blue) and YO-PRO-1 (green) staining at 24 h after H2O2. RGC-5 were immersed in serum-free DMEM and then propolis PE (extract with ethanol) or propolis PW (extract with water) was added to the cultures. Cells, which were maintained in this condition for 24 h, were grouped as described below. (A) Non-treated cells showed normal nuclear morphology and (E) were negative for YO-PRO-1 (early-stage apoptotic and necrotic cells are YO-PRO-1-positive). (B) H2O2 (0.3 mM)-induced neurotoxicity, with cells showing condensation and fragmentation of their nuclei, including YO-PRO-1-positively stained cells (F). (C) Pretreatment with 3 µg ml−1 PE or 1 µg ml−1 PW at 1 h before H2O2 (0.3 mM)-treatment reduced both nuclear condensation (C and D, respectively) and YO-PRO-1-positive staining (G and H, respectively). A and E: control; B and F: vehicle-treatment plus H2O2; C, G: propolis PE at 3 µg ml−1 plus H2O2; D and H: propolis PW at 1 µg ml−1 plus H2O2; A–D: Hoechst 33342 staining; E–H: YO-PRP-1 staining; I: the number of cells exhibiting YO-PRO-1 fluorescence was counted, and positive cells were expressed as the percentage of YO-PRO-1-positive to Hoechst 33342-positive cells. Viable cells are Hoechst 33342-positive and YO-PRO-1-negative, whereas dead cells are Hoechst 33342-positive and YO-PRO-1-positive. Non-treated cells showed normal nuclear morphology and were negative for YO-PRO-1. H2O2-treated cells showed shrinkage and condensation of their nuclei, including YO-PRO-1-positive cells. Treatment with propolis (PE or PW) reduced both nuclei shrinkage and YO-PRO-1-positive staining. Each column represents the mean ± SEM, n = 8. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus H2O2-treatment alone.