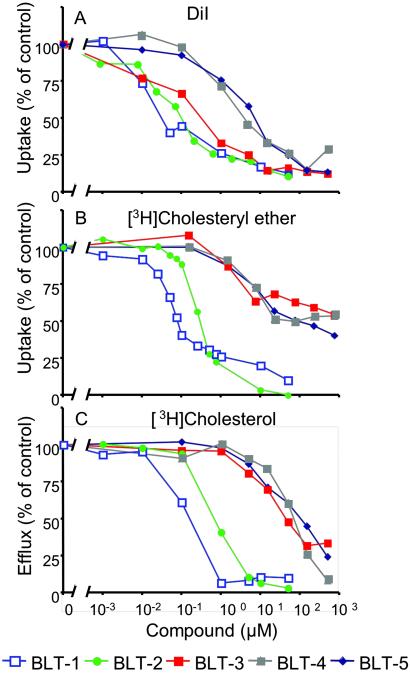
Fig 2.
Concentration dependence of the inhibition by BLTs of SR-BI-mediated lipid transfer between HDL and cells. ldlA[mSR-BI] cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of BLTs, and their effects on DiI uptake from DiI-HDL (A), [3H]CE uptake from [3H]CE-HDL (B), and the efflux of [3H]cholesterol from cells to HDL (C) were determined. The 100% of control values were 50.6 ng of HDL protein equivalents per well (384-well plates) (A) and 3,908 ng of HDL protein equivalents per mg of cellular protein (B). In C, the data were normalized such that the maximum amount of [3H]cholesterol transferred from cells to HDL in the absence of compounds (55.7% of total) was set to 100%. The 0% value corresponds to the efflux of [3H]cholesterol transferred from ldlA[mSR-BI] cells to HDL without BLTs and in the presence of saturating inhibitory amounts of the specific anti-SR-BI blocking antibody KKB-1 (15% of total) (20). The efflux of [3H]cholesterol from ldlA-7 cells measured in the absence or presence of KKB-1 was 15% and 10% of total cellular [3H]cholesterol, respectively.