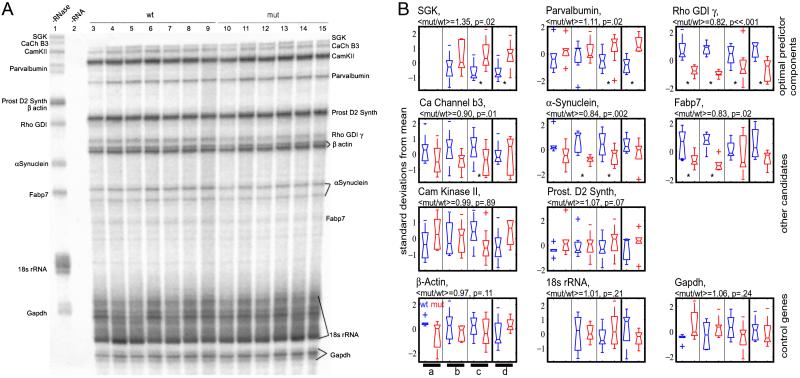
Fig. 2.
(A) Representative RNase protection assay. Shown are the same samples used for the P63 Mecp21/y vs. Mecp2+/y, cerebral cortex microarray experiment (Table 1, experiment 6). Lane 1 is a 1/5 loading of the −RNase control. Lane 2 shows the −sample +RNase control. Lanes 3–9 are the wild-type cerebral cortex samples; lanes 10–15 are the mutant samples. (B) Bands from four separate RNase protection experiments were quantitated by phosphorimaging, the results were converted to z-scores (i.e., standardized), and the results are presented. Plots were generated by matlab boxplot function. Briefly, the median is the horizontal line inside each box, the interquartile range is represented by the box, the ranges of the data are represented by the whiskers, and any outliers are represented by crosses. Each pair of boxes represents an experiment; wild-type samples are in blue, mutants are in red. Experiment a: Mecp21lox/y (n = 6) vs. Mecp2+/y (n = 6), P40–60 cerebral cortex. Experiment b: Mecp21lox/y (n = 7) vs. Mecp2+/y (n = 6), P63 cerebral cortex (Table 1, experiment 6). Experiment c: Mecp22lox/y, Cam Kinase Cre 93+/o (n = 9) vs. Mecp2+/y (n = 9), P135–180 cerebral cortex (Table 1, experiment 8). Experiment d: Mecp21lox/y (n = 5) vs. Mecp2+/y (n = 6), P40–60 hippocampus. Asterisks denote comparisons that are statistically significant (P < 0.05 by two-tailed t test). Above each plot are shown the ratio of the means of mutant to wild type for all of the cerebral cortex samples (experiments a–c, n = 43) as well as the results of a two-tailed Wilcoxon signed rank test on the combined standardized data. The genes' data are organized according to their origin as candidates: the top three genes were components of the optimal predictor (Fig. 1) and the next five plots were candidates because of their appearance in other significantly successful predictors, or due to significant VERA/SAM or t test scores. The bottom three plots represent the loading controls used.