Fig 3.
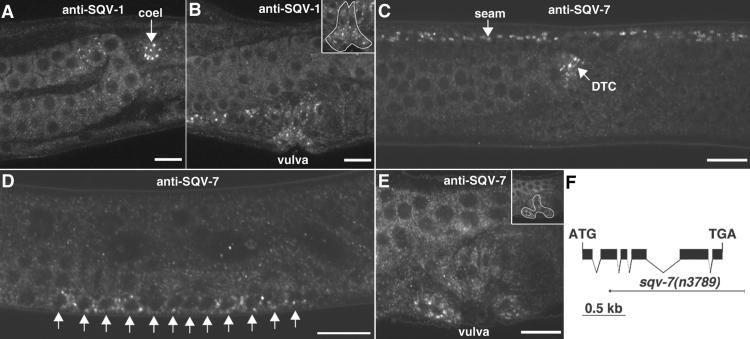
SQV-1 and SQV-7 localize to punctate cytoplasmic sites. (A and B) Whole-mount staining of WT animals by using anti-SQV-1-MBP rabbit polyclonal Abs. SQV-1 Abs localize to punctate cytoplasmic foci. (A) SQV-1 staining of a coelomocyte (coel) in an L4 larva is indicated by a white arrow. (B) SQV-1 staining of vulval cells during vulval morphogenesis. (Inset) The location of the vulval cells is indicated. (C–E) Whole-mount staining of WT animals by using anti-SQV-7 peptide Abs. SQV-7 Abs localize to punctate cytoplasmic foci. (C) SQV-7 staining in seam cells (seam) and the distal tip cell (DTC) in an L4 larva. Seam cells form a lateral line along the length of the worm from head to tail. The distal tip cell is located at the end of the developing gonad, which is visible to the left of the DTC. (D) SQV-7 staining in the 12 vulval precursor cells in an L3 larva. Ten of these 12 cells will divide once more to generate the 22 vulval descendants that form the vulva. (E) SQV-7 staining in vulval cells during vulval morphogenesis in an L4 larva. A subset of the 22 vulval cells is visible in this focal plane. (F) Deletion allele of sqv-7. The structure of the sqv-7 gene is shown by using solid boxes to indicate exons. The initiation and termination codons are indicated. The sqv-7(n3789) deletion is shown by using a thin solid line to depict the extent of the deletion and a short thick solid line to depict the extent of the duplication (see Materials and Methods). (Bars = 10 μm.)