Abstract
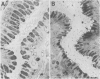
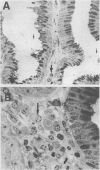
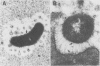
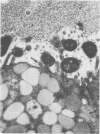
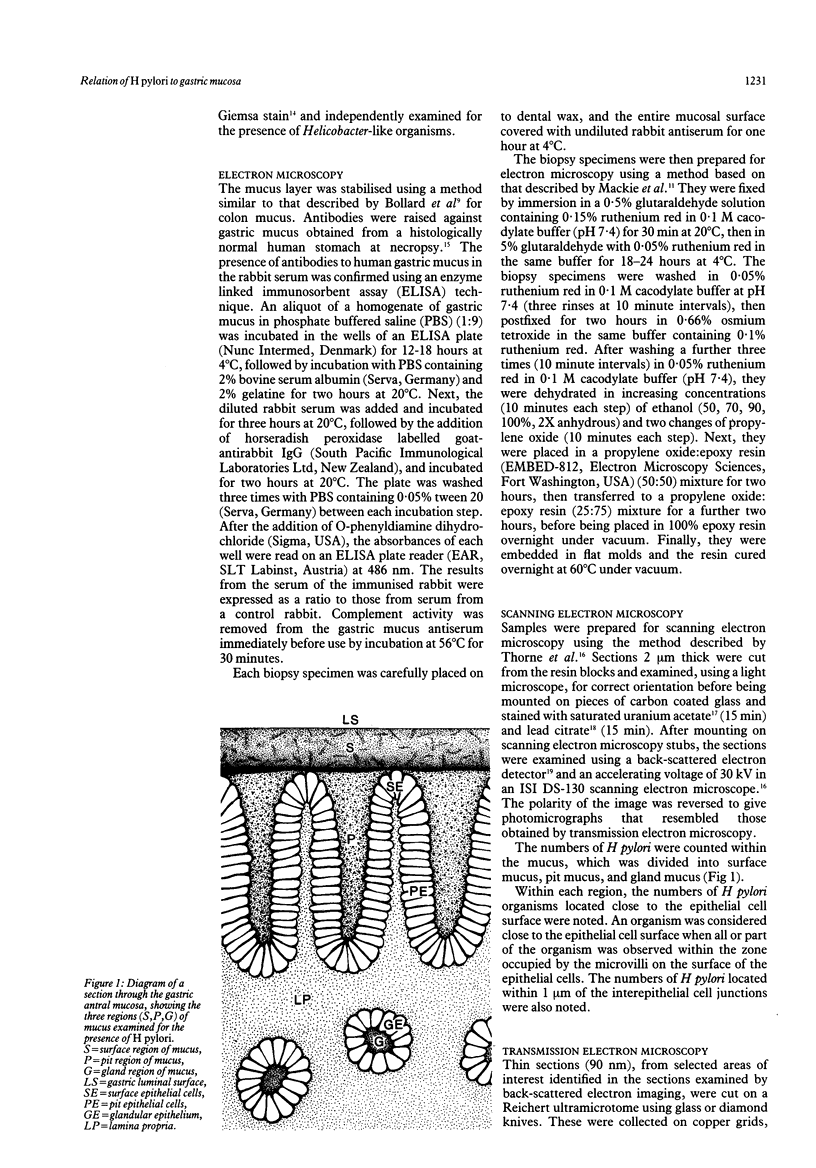
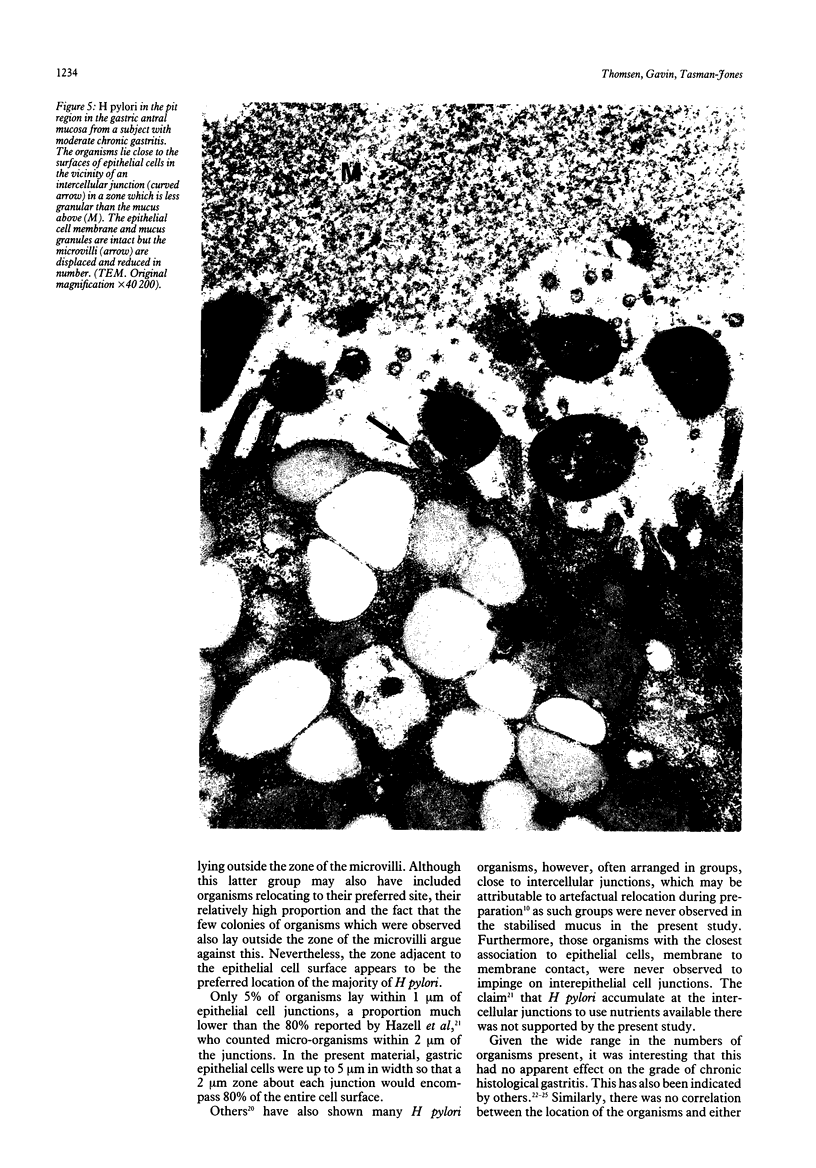
The spatial relations between bacteria and the affected tissues can indicate pathogenic mechanisms. This study was undertaken to define the spatial relation of Helicobacter pylori to the human gastric mucosa. Antibodies against gastric mucus and ruthenium red were used to stabilise the glycoprotein structure of the mucus and glycocalyces in antral biopsy specimens from eight patients infected with H pylori. The location of organisms and ultrastructural features were assessed using systematic scanning and transmission electron microscopy: 92 (2)% (mean (SE] of H pylori were in the pit mucus, and 7 (3)% were in the surface mucus; 60 (12)% of H pylori were close to epithelial cells, with only 5 (2)% located near the epithelial intercellular junctions. Fine filamentous strands extended between organisms and nearby epithelial cells, with few organisms in membrane to membrane contact. H pylori were not observed between, beneath, or within cells of the gastric mucosa. The preferred location of H pylori in the gastric antrum is within the pit mucus close to the epithelial cell surface, with no evidence that they have a direct toxic effect on the mucosa.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Gastric Campylobacter-like organisms, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode G., Malfertheiner P., Ditschuneit H. Pathogenetic implications of ultrastructural findings in Campylobacter pylori related gastroduodenal disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1988;142:25–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollard J. E., Vanderwee M. A., Smith G. W., Tasman-Jones C., Gavin J. B., Lee S. P. Location of bacteria in the mid-colon of the rat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):604–608. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.604-608.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The role of bacterial surface structures in pathogenesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1981;8(4):303–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418109085082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Avots-Avotins A. E., Fader R. C. Evidence for a bladder cell glycolipid receptor for Escherichia coli and the effect of neuraminic acid and colominic acid on adherence. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):944–948. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.944-948.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R. Mechanisms of association of bacteria with mucosal surfaces. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:36–55. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. F., Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J. Simplified techniques for identifying Campylobacter pyloridis. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;39(11):1279–1279. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.11.1279-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Borody T. J., Gal A., Lee A. Campylobacter pyloridis gastritis I: Detection of urease as a marker of bacterial colonization and gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Apr;82(4):292–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Lee A., Brady L., Hennessy W. Campylobacter pyloridis and gastritis: association with intercellular spaces and adaptation to an environment of mucus as important factors in colonization of the gastric epithelium. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. J., Reed P. I., Ali M. H. Campylobacter like organisms in duodenal and antral endoscopic biopsies: relationship to inflammation. Gut. 1986 Oct;27(10):1132–1137. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.10.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Lessells A. M., Eldridge J. Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1002–1006. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Maher K., Thomsen L., Miller M., Nicholson G., Tasman-Jones C. Distribution of Campylobacter pylori in the human stomach obtained at postmortem. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Apr;23(3):257–264. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Nicholson G. Ingestion of Campylobacter pyloridis causes gastritis and raised fasting gastric pH. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Nicholson G., Lloyd G., Haines D., Rogers A., Taylor D. Seroepidemiology of Campylobacter pyloridis. N Z Med J. 1986 Sep 10;99(809):657–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Levi J., Dolby J. M., Dunscombe P. L., Smith A., Clark J., Stephenson M. L. Campylobacter pyloridis in peptic ulcer disease: microbiology, pathology, and scanning electron microscopy. Gut. 1985 Nov;26(11):1183–1188. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.11.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollason T. P., Stone J., Rhodes J. M. Spiral organisms in endoscopic biopsies of the human stomach. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;37(1):23–26. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen L., Tasman-Jones C., Morris A., Wiggins P., Lee S., Forlong C. Ammonia produced by Campylobacter pylori neutralizes H+ moving through gastric mucus. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989 Aug;24(6):761–768. doi: 10.3109/00365528909093119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne P. R., Vujcich T. E., Gavin J. B. Back-scattered electron imaging of sections through the cochlea: a new technique for studying cochlear morphology. Stain Technol. 1987 May;62(3):191–199. doi: 10.3109/10520298709107991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R., Truelove S. C., Gear M. W. The histological diagnosis of chronic gastritis in fibreoptic gastroscope biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Heatley R. V. Local immune response to gastric Campylobacter in non-ulcer dyspepsia. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;39(8):863–870. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.8.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafriri D., Oron Y., Eisenstein B. I., Ofek I. Growth advantage and enhanced toxicity of Escherichia coli adherent to tissue culture cells due to restricted diffusion of products secreted by the cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1210–1216. doi: 10.1172/JCI112939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]