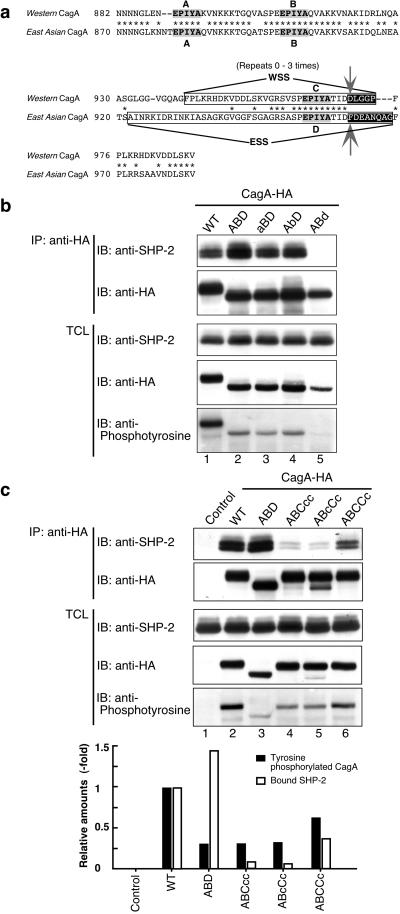
Fig 3.
Identification and functional characterization of East Asian CagA-specific sequence for tyrosine phosphorylation. (a) Sequence alignment of the EPIYA regions for Western (11637 strain) and East Asian CagA proteins. The Western CagA-specific sequence (WSS) and the East Asian (F32 strain) CagA-specific sequence (ESS) are boxed. Nonconserved residues at the C-terminal regions of EPIYA-C and EPIYA-D are black-boxed. Arrows indicate residues replaced for generation of ABC970DFcc and ABD961FD mutants of CagA. (b and c) AGS cells were transfected with WT-CagA, EPIYA mutant, or a control empty vector. CagA proteins were immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates with anti-HA. The immunoprecipitates (IP) and total cell lysates (TCL) were immunoblotted (IB) with antibodies as described. Protein expression levels of each CagA variants were normalized with band intensities obtained from anti-HA immunoblotting. The relative amounts of tyrosine phosphorylated CagA (black bars) and CagA-bound SHP-2 (white bars) were calculated with the values for WT 11637-CagA taken as 1. The aBD, AbD, and ABd variants were generated from ABD by replacing tyrosine residues constituting EPIYA-A, -B, and -D with alanine residues, respectively.