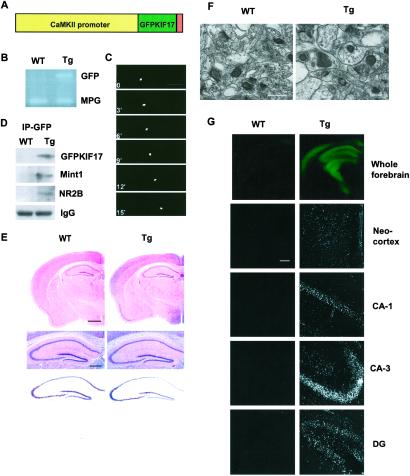
Fig 1.
Construction and histological characterization of GFPKIF17 transgenic mice. (A) The construct for production of GFPKIF17 transgenic mice. (B) PCR screening with GFP primers, using endogenous MPG as internal control. (C) Visualization of motility of GFPKIF17. (Bar = 20 μm.) (D) Immunoprecipitation of the forebrain fraction from mouse using anti-GFP antibody; the same immunoblot was used for antibodies against KIF17, Mint 1(mLin10), NR2B, and IgG. (E) Normal brain morphology in transgenic mice compared with WT, hematoxylin/eosin staining (Top), higher magnification of the hematoxylin/eosin staining (Middle), and Nissl staining (Bottom) of the hippocampus. (Bars = 500 μm.) (F) The ultrastructure of axospinous synapses in CA1 hippocampus shown in each case. (Bar = 10 μm.) (G) GFPKIF17 localization in forebrain region of mice. Neocortex and hippocampal subregions (CA1, CA3, DG). (Bar = 100 μm.)