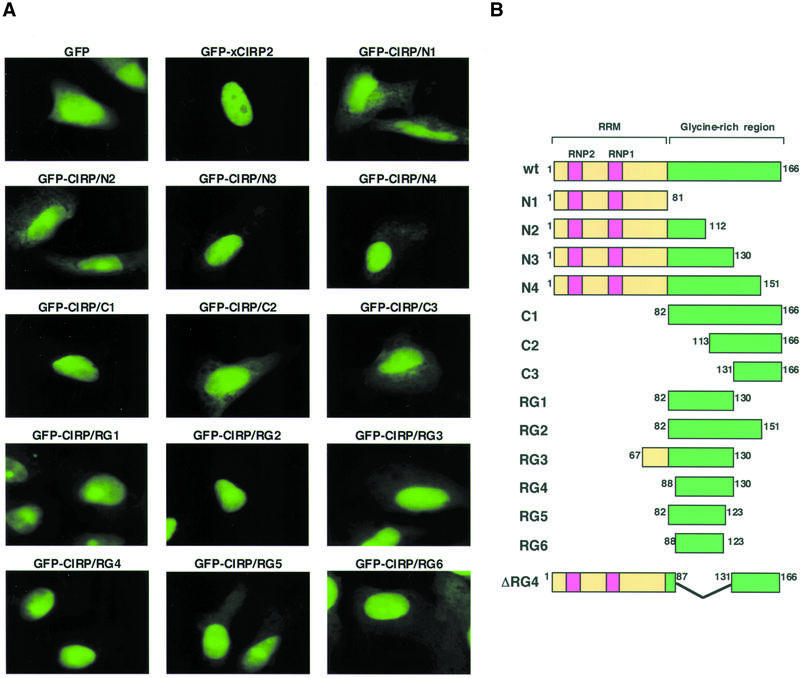
Figure 3.
Identification of the domain, which functions as a nuclear localization signal. (A) Fluorescent micrographs showing subcellular localization of GFP and the GFP-xCIRP2 derivatives. HeLa S3 cells were transfected with plasmid DNA to express GFP fusion xCIRP2 derivatives. The localization of the GFP fusion proteins was examined under a fluorescence microscope. (B) Schematic diagrams of xCIRP2 protein and its deletion mutants expressed in HeLa S3 cells. GFP is fused at the N-terminus of xCIRP2.