Abstract
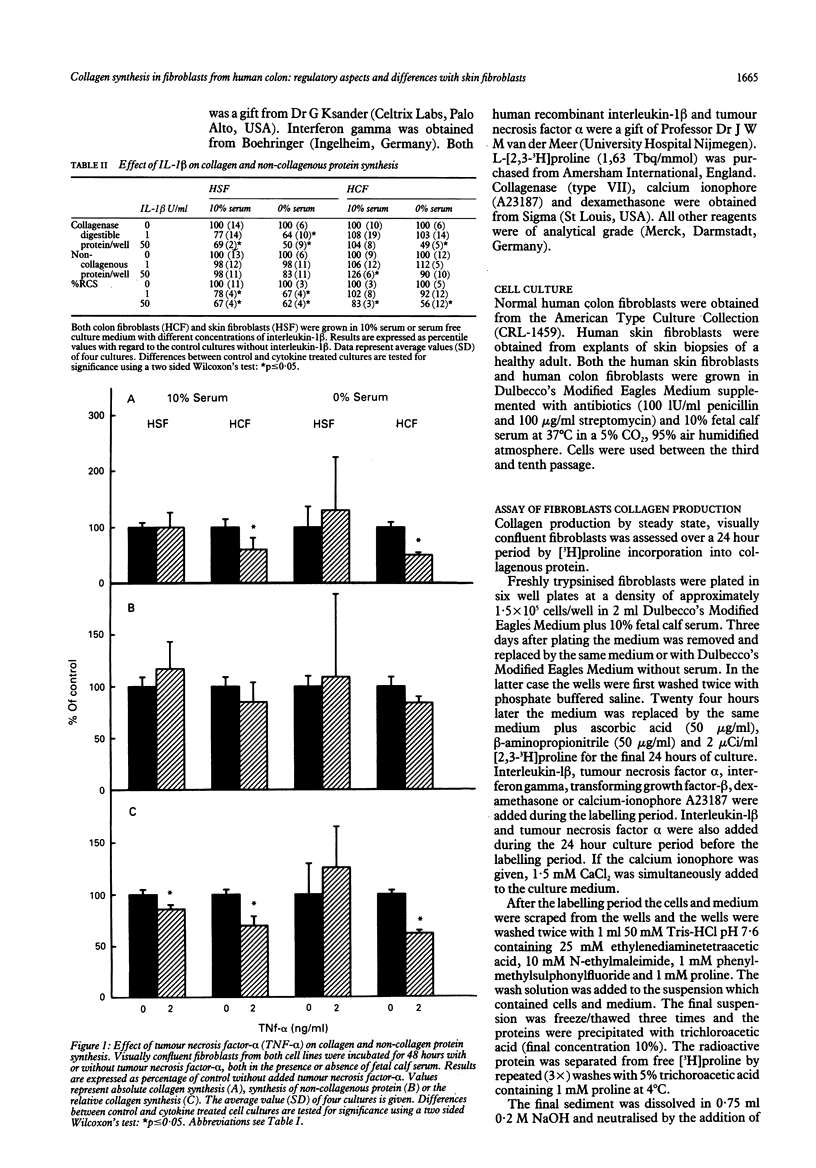
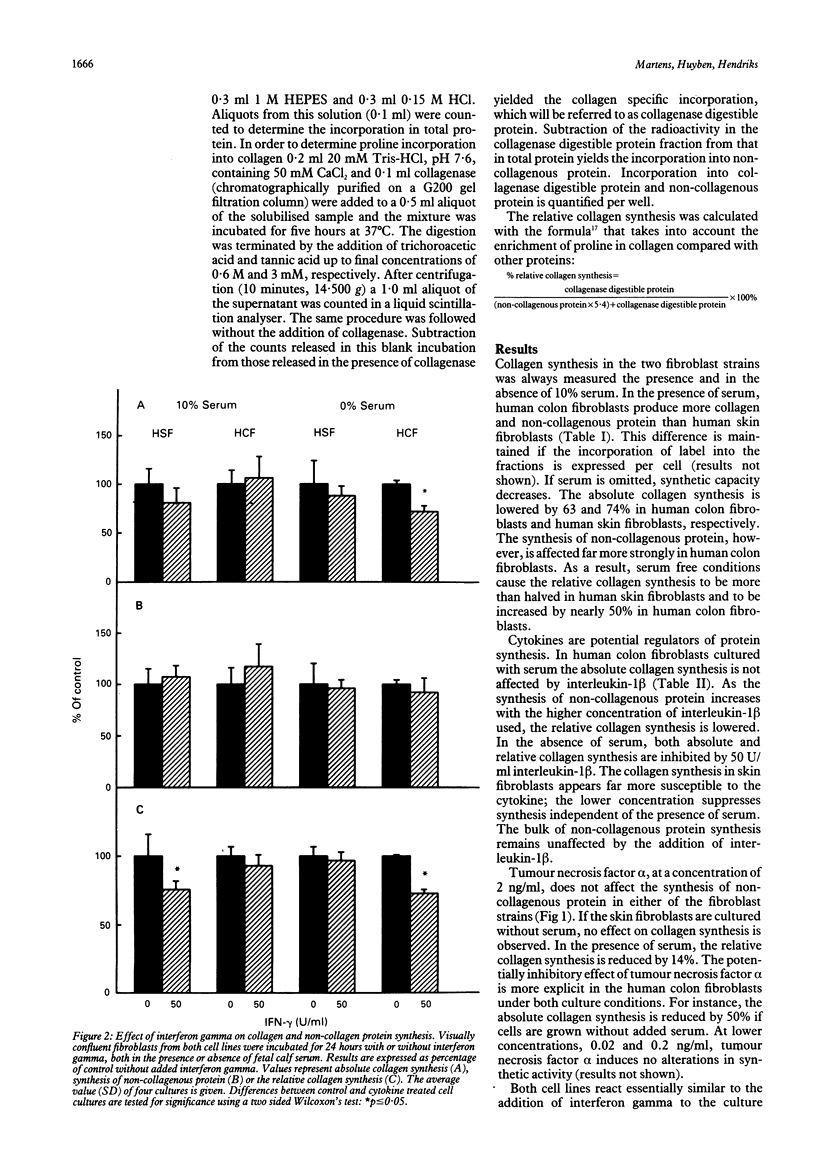
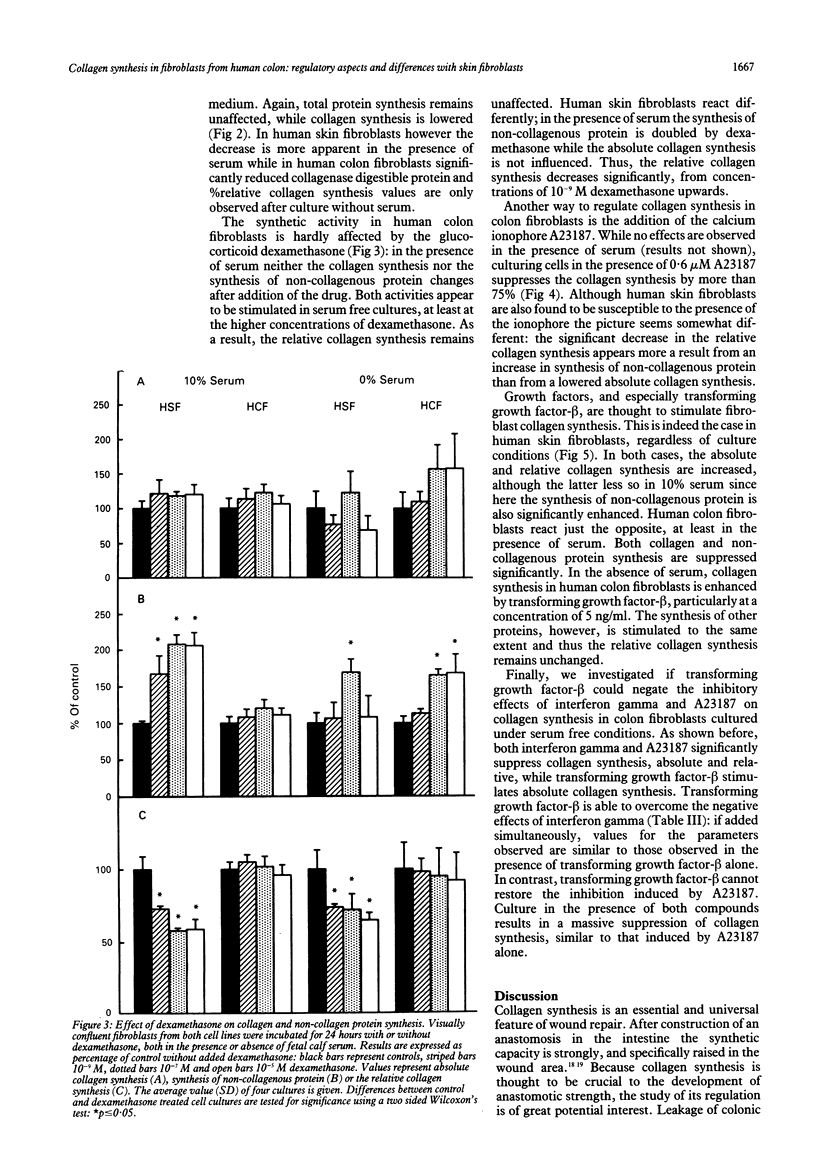
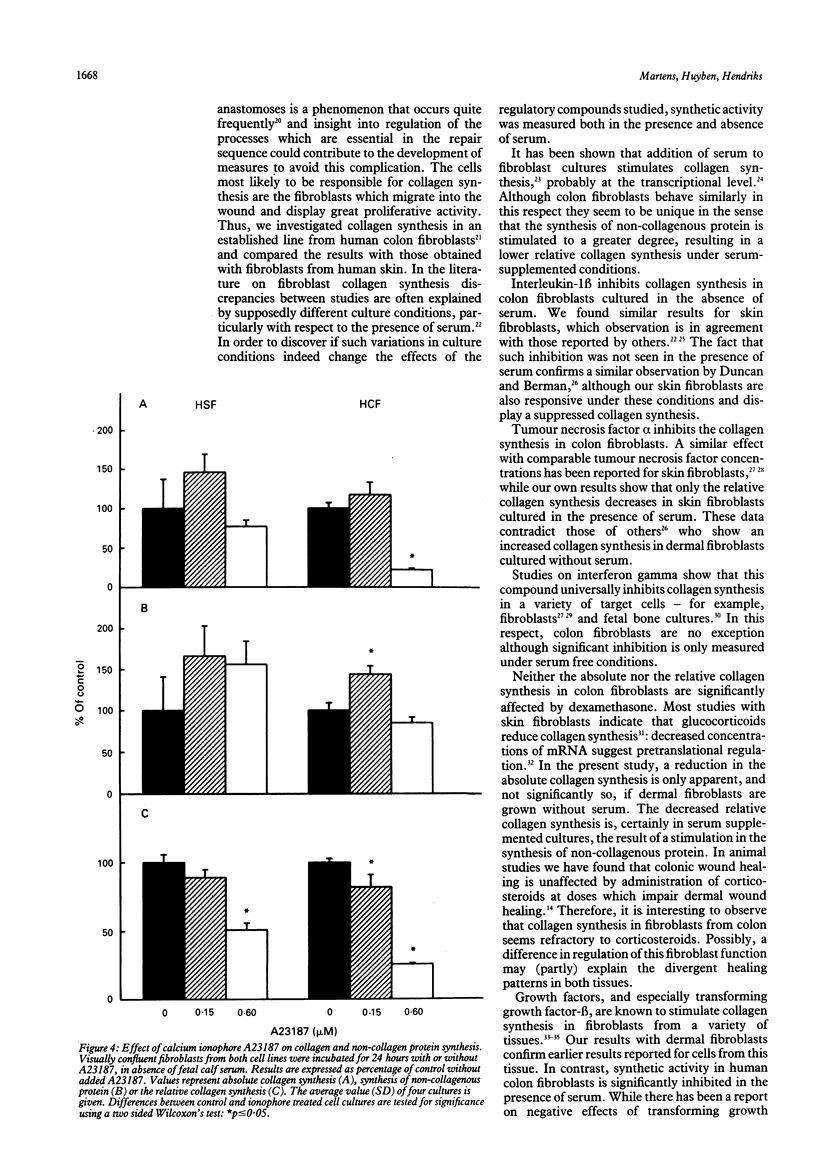
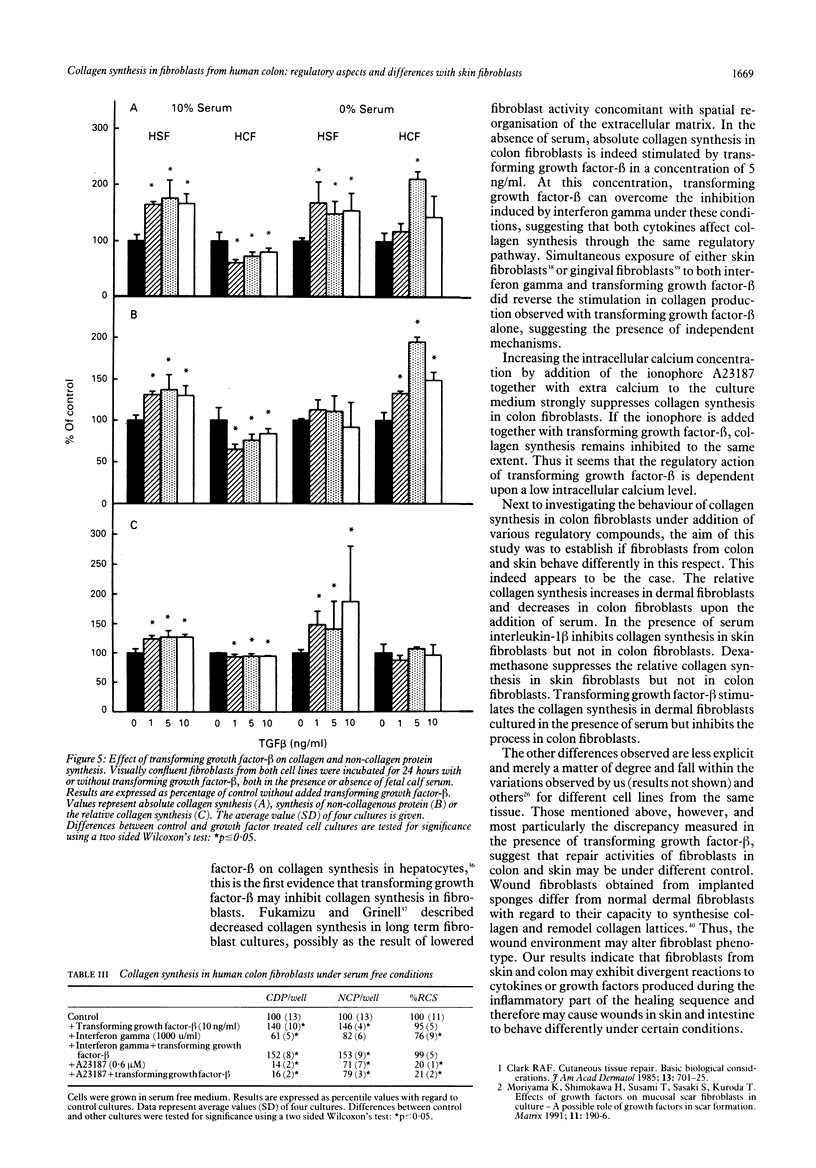
The purpose of this study was to examine regulation of collagen synthesis in human colon fibroblasts and compare the results from colon fibroblasts with those obtained in fibroblasts from human skin. The effects of interleukin-1 beta, tumour necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, transforming growth factor-beta, dexamethasone, and the calcium ionophore A23187 were investigated. All compounds were tested both in the absence and in the presence of fetal calf serum in the culture medium. The process of collagen synthesis in fibroblasts from colon and skin appears to be affected differently by these regulatory compounds. The most pronounced differences were that the relative collagen synthesis increased in dermal fibroblasts and decreased in colon fibroblasts upon addition of serum. In the presence of serum, interleukin-1 beta inhibited collagen synthesis in skin fibroblasts but not in colon fibroblasts. Dexamethasone suppressed the relative collagen synthesis in skin fibroblasts but not in colon fibroblasts. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulated the collagen synthesis in dermal fibroblasts in the presence of serum, but inhibited the process in colon fibroblasts. Because fibroblasts are the primary sources of collagen needed during wound repair, these results may offer (part of) the explanation why wounds in skin and intestine appear to behave differently under certain conditions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrez M. V., Chua F. K. The role of colon fibroblasts in malignant large bowel obstruction--an experimental in vitro model. Br J Cancer. 1990 Oct;62(4):567–572. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu M., Diegelmann R., Oliver N. Fibronectin is overproduced by keloid fibroblasts during abnormal wound healing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1642–1650. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar R., Penfornis H., Mauviel A., Loyau G., Saklatvala J., Pujol J. P. Interleukin-1 inhibits the synthesis of collagen by fibroblasts. Biochem Int. 1986 Oct;13(4):709–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Polak K. L., Uitto J. Collagen biosynthesis by human skin fibroblasts. I. Optimization of the culture conditions for synthesis of type I and type III procollagens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 28;607(1):145–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braskén P., Renvall S., Sandberg M. Fibronectin and collagen gene expression in healing experimental colonic anastomoses. Br J Surg. 1991 Sep;78(9):1048–1052. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. Cutaneous tissue repair: basic biologic considerations. I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985 Nov;13(5 Pt 1):701–725. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(85)70213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doillon C. J., Dunn M. G., Bender E., Silver F. H. Collagen fiber formation in repair tissue: development of strength and toughness. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Dec;5(6):481–492. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. R., Berman B. Differential regulation of collagen, glycosaminoglycan, fibronectin, and collagenase activity production in cultured human adult dermal fibroblasts by interleukin 1-alpha and beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha and beta. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 May;92(5):699–706. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12696891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eghbali M., Tomek R., Sukhatme V. P., Woods C., Bhambi B. Differential effects of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and phorbol myristate acetate on cardiac fibroblasts. Regulation of fibrillar collagen mRNAs and expression of early transcription factors. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):483–490. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest L. Current concepts in soft connective tissue wound healing. Br J Surg. 1983 Mar;70(3):133–140. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu H., Grinnell F. Spatial organization of extracellular matrix and fibroblast activity: effects of serum, transforming growth factor beta, and fibronectin. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Oct;190(2):276–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90197-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata R., Sunada H., Arai K., Sato T., Ninomiya Y., Nagai Y., Senoo H. Regulation of collagen metabolism and cell growth by epidermal growth factor and ascorbate in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 15;173(2):261–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks T., Mastboom W. J. Healing of experimental intestinal anastomoses. Parameters for repair. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 Oct;33(10):891–901. doi: 10.1007/BF02051930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Freundlich B., Rosenbloom J. Selective inhibition of human diploid fibroblast collagen synthesis by interferons. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):1112–1116. doi: 10.1172/JCI111480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laato M., Kähäri V. M., Niinikoski J., Vuorio E. Epidermal growth factor increases collagen production in granulation tissue by stimulation of fibroblast proliferation and not by activation of procollagen genes. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):385–388. doi: 10.1042/bj2470385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. W., Peacock E. E., Jr Studies on the biology of collagen during wound healing. I. Rate of collagen synthesis and deposition in cutaneous wounds of the rat. Surgery. 1968 Jul;64(1):288–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens M. F., Hendriks T. Postoperative changes in collagen synthesis in intestinal anastomoses of the rat: differences between small and large bowel. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1482–1487. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch C., Hatamochi A., Scharffetter K., Krieg T. Regulation of collagen synthesis in fibroblasts within a three-dimensional collagen gel. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Oct;178(2):493–503. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A., Daireaux M., Rédini F., Galera P., Loyau G., Pujol J. P. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits collagen and fibronectin synthesis in human dermal fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A., Heino J., Kähäri V. M., Hartmann D. J., Loyau G., Pujol J. P., Vuorio E. Comparative effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on collagen production and corresponding procollagen mRNA levels in human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Feb;96(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama K., Shimokawa H., Susami T., Sasaki S., Kuroda T. Effects of growth factors on mucosal scar fibroblasts in culture--a possible role of growth factors in scar formation. Matrix. 1991 Jun;11(3):190–196. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan A. S., Page R. C. Serum regulation of collagen biosynthesis in human diploid fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan A. S., Page R. C., Swanson J. Collagen synthesis by human fibroblasts. Regulation by transforming growth factor-beta in the presence of other inflammatory mediators. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):463–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2600463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen A. I., Uitto J., Oikarinen J. Glucocorticoid action on connective tissue: from molecular mechanisms to clinical practice. Med Biol. 1986;64(5):221–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen A., Vuorio E., Vuorio T. Comparison of the effects of dexamethasone and 13-cis-retinoic acid on connective tissue biosynthesis in human skin fibroblasts. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281(4):273–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00431062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Raghow R., Stricklin G. P., Poppleton H., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Modulation of fibroblast functions by interleukin 1: increased steady-state accumulation of type I procollagen messenger RNAs and stimulation of other functions but not chemotaxis by human recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and beta. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):311–318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu G., Masta S., Meyers D., Narayanan A. S. Collagen synthesis by normal and fibrotic human lung fibroblasts and the effect of transforming growth factor-beta. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jul;140(1):95–100. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan M. C., Kirk S. J., Wasserkrug H. L., Barbul A. The wound environment as a regulator of fibroblast phenotype. J Surg Res. 1991 May;50(5):442–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90022-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharffetter K., Heckmann M., Hatamochi A., Mauch C., Stein B., Riethmüller G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Krieg T. Synergistic effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma on collagen synthesis of human skin fibroblasts in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. D., Gowen M., Mundy G. R. Effects of interferon-gamma and other cytokines on collagen synthesis in fetal rat bone cultures. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2494–2499. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. Recovery and tissue repair. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jul;41(3):295–301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi Y., Kakumu S., Yoshioka K., Arao M., Inoue M., Wakita T. Effects of various cytokines on collagen synthesis by normal rat hepatocytes in primary cultures and fibroblasts. Digestion. 1989;44(4):191–199. doi: 10.1159/000199911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Olsen A., Herhal J., Constantine G., Rosenbloom J., Jimenez S. A. Interferon-gamma reverses the stimulation of collagen but not fibronectin gene expression by transforming growth factor-beta in normal human fibroblasts. Eur J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;20(5):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1990.tb01890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Rosenbloom J., Jimenez S. A. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) causes a persistent increase in steady-state amounts of type I and type III collagen and fibronectin mRNAs in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):597–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2470597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


