Abstract
5-Aminosalicylic acid (5ASA), 4ASA, their N-acetylated metabolites N-acetyl-5ASA and N-acetyl-4ASA, olsalazine, and colchicine impair interferon-gamma (IFN gamma) induced HLA-DR expression on a colonic cell line, HT-29. The mechanism of this effect is now reported. HT-29 cells were cultured with 50 U/ml IFN gamma with or without drug, and northern blot analysis was performed using a probe for the beta chain of the DR molecule. IFN gamma led to a noticeable increase in HLA-DR mRNA which was attenuated by the drugs. Analysis of the specific binding of increasing concentrations of 125I-IFN gamma by non-linear regression showed a Kd of 1.35 x 10(-10) M and 2.3 x 10(5) binding sites per HT-29 cell. Binding of 125I-IFN gamma was reduced by incubation with increasing concentrations of unlabelled IFN gamma but not with IFN alpha. Incubation with therapeutic concentrations of drugs led to the following reductions in binding: 10 mM 5ASA, 20% (p < 0.001); 10 mM N-acetyl-5ASA, 24% (p < 0.01); 10 mM 4ASA, 21% (p < 0.005); 10 mM N-acetyl-4ASA, 29% (p < 0.001); and 1 mM olsalazine, 29% (p < 0.001). Colchicine (10(-7) M) and 10(-5) M prednisolone had no effect. Incubation with higher concentrations of the drugs revealed a dose-response effect on binding with complete inhibition by 100 mM 4ASA and 10 mM olsalazine, and lesser degrees of inhibition by 100 mM 5ASA, N-acetyl-5ASA, and N-acetyl-4ASA. At concentrations found in the rectal lumen, the salicylates used in inflammatory bowel disease impair the binding of IFN gamma to its receptor on colonic epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF

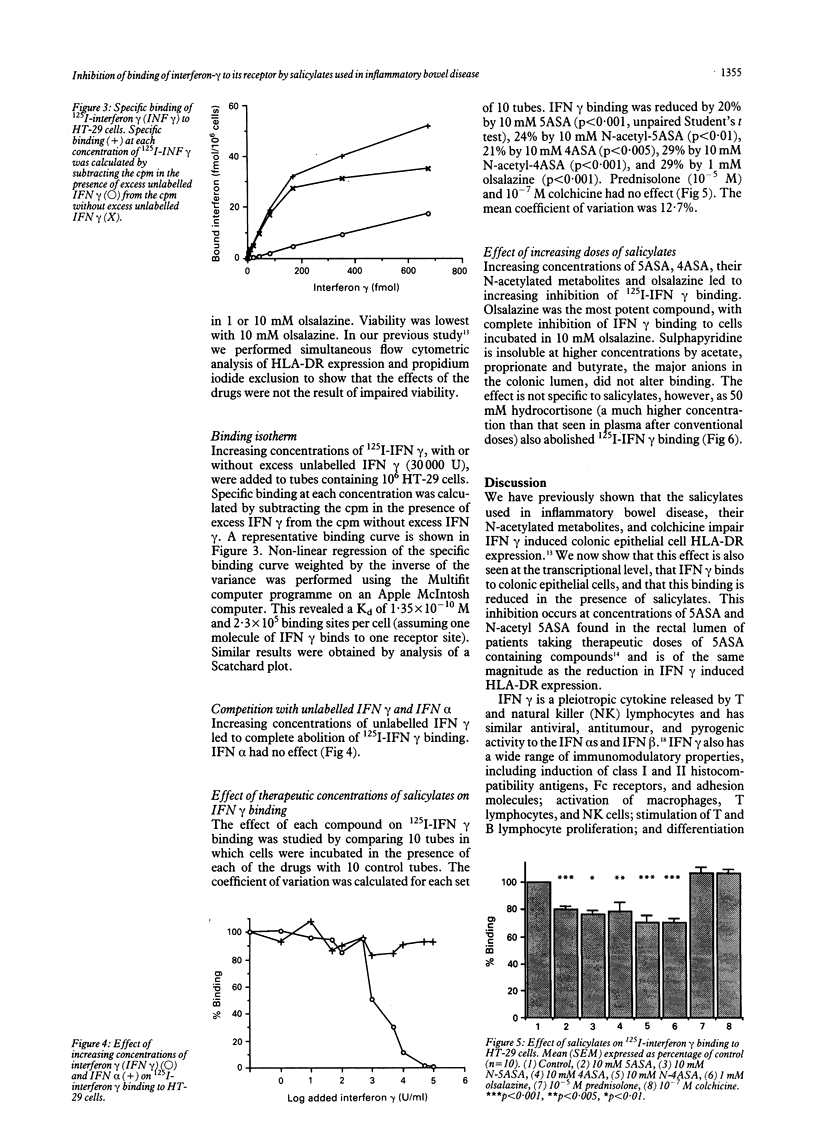
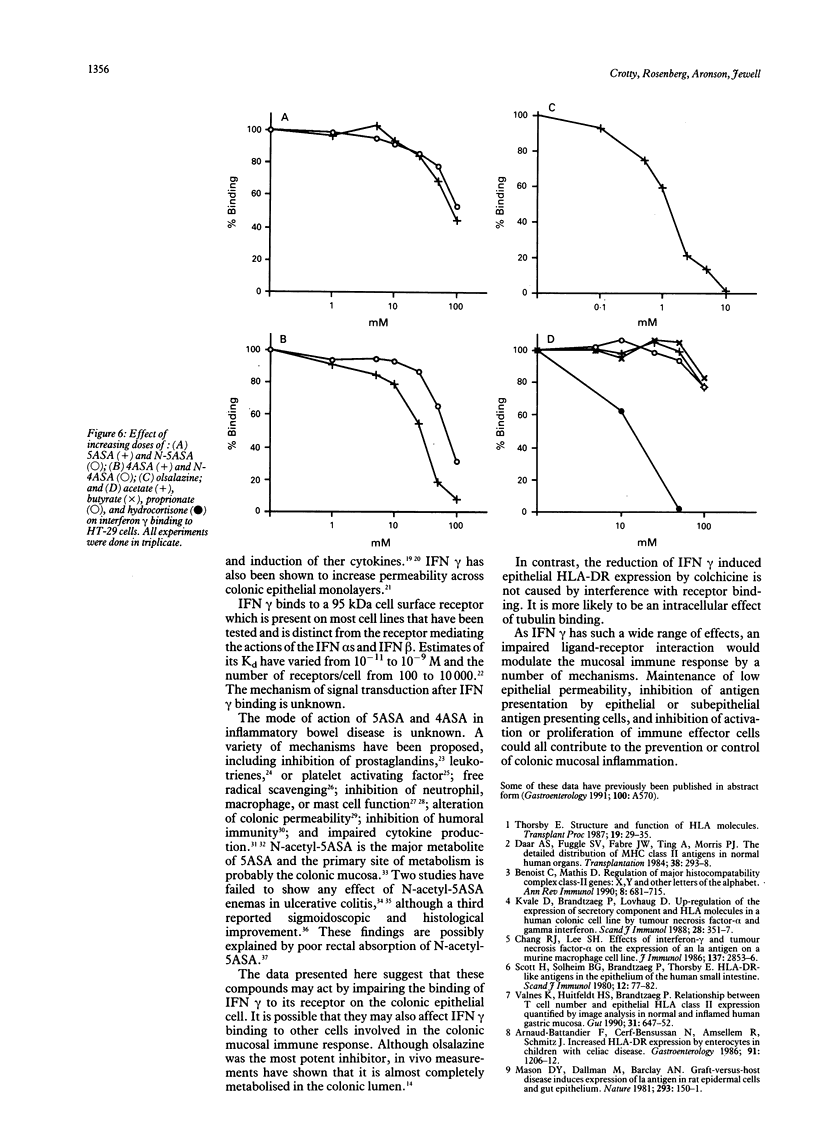

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud-Battandier F., Cerf-Bensussan N., Amsellem R., Schmitz J. Increased HLA-DR expression by enterocytes in children with celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1206–1212. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R. Interferons. Lancet. 1989 May 13;1(8646):1060–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett K. E., Tashof T. L., Metcalfe D. D. Inhibition of IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation by sulphasalazine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 2;107(2):279–281. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Mathis D. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class-II genes: X, Y and other letters of the alphabet. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:681–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. J., Lee S. H. Effects of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the expression of an Ia antigen on a murine macrophage cell line. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2853–2856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotty B., Hoang P., Dalton H. R., Jewell D. P. Salicylates used in inflammatory bowel disease and colchicine impair interferon-gamma induced HLA-DR expression. Gut. 1992 Jan;33(1):59–64. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of MHC Class II antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Karmeli F., Razin E., Rachmilewitz D. Role of platelet-activating factor in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine and prednisolone. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1167–1172. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C. J., Lo Casto M. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase in human rectal mucosa. Gut. 1983 Mar;24(3):213–217. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.3.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland A., Jewell D. P. Mechanism of action of 5-aminosalicylic acid and its derivatives. Clin Sci (Lond) 1990 Feb;78(2):119–125. doi: 10.1042/cs0780119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvale D., Brandtzaeg P., Løvhaug D. Up-regulation of the expression of secretory component and HLA molecules in a human colonic cell line by tumour necrosis factor-alpha and gamma interferon. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Sep;28(3):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Pestka S. Interferon receptors. Immunol Today. 1988 Dec;9(12):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritsen K., Hansen J., Ryde M., Rask-Madsen J. Colonic azodisalicylate metabolism determined by in vivo dialysis in healthy volunteers and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1496–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Schloemann S. R., Bertovich M. J., Nash G. S., Peters M., Stenson W. F. Inhibition of antibody secretion by 5-aminosalicylic acid. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):442–448. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91569-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):724–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI113938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Lamming C. E., Gallagher A., Hawthorne A. B., Hawkey C. J. 5-Aminosalicylic acid is a potent inhibitor of interleukin 1 beta production in organ culture of colonic biopsy specimens from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):50–54. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M., Barclay A. N. Graft-versus-host disease induces expression of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):150–151. doi: 10.1038/293150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. B., Jewell D. P. Class II antigen (HLA-DR) expression by intestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory diseases of colon. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;40(3):312–317. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.3.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Garra A. Interleukins and the immune system 2. Lancet. 1989 May 6;1(8645):1003–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92640-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup M. E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of prednisone and prednisolone. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1979 Mar-Apr;4(2):111–128. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197904020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Solheim B. G., Brandtzaeg P., Thorsby E. HLA-DR-like antigens in the epithelium of the human small intestine. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(1):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Mason D. Y., Jewell D. P. Expression of HLA-DR antigens by colonic epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):614–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson W. F., Lobos E. Sulfasalazine inhibits the synthesis of chemotactic lipids by neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):494–497. doi: 10.1172/JCI110474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson W. F., Mehta J., Spilberg I. Sulfasalazine inhibition of binding of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) to its receptor on human neutrophils. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Feb 1;33(3):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsby E. Structure and function of HLA molecules. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valnes K., Huitfeldt H. S., Brandtzaeg P. Relation between T cell number and epithelial HLA class II expression quantified by image analysis in normal and inflamed human gastric mucosa. Gut. 1990 Jun;31(6):647–652. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.6.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby C. P., Piris J., Truelove S. C. The effect of topical N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid in ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(6):715–719. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hogezand R. A., van Hees P. A., van Gorp J. P., van Lier H. J., Bakker J. H., Wesseling P., van Haelst U. J., van Tongeren J. H. Double-blind comparison of 5-aminosalicylic acid and acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid suppositories in patients with idiopathic proctitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Feb;2(1):33–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1988.tb00668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Ritter C., Grisham M. B., Granger D. N. Sulfasalazine metabolites and dapsone attenuate formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced mucosal injury in rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1989 Mar;96(3):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



